⚖️ Judicial Backlog in India: A Growing Crisis in the Justice System
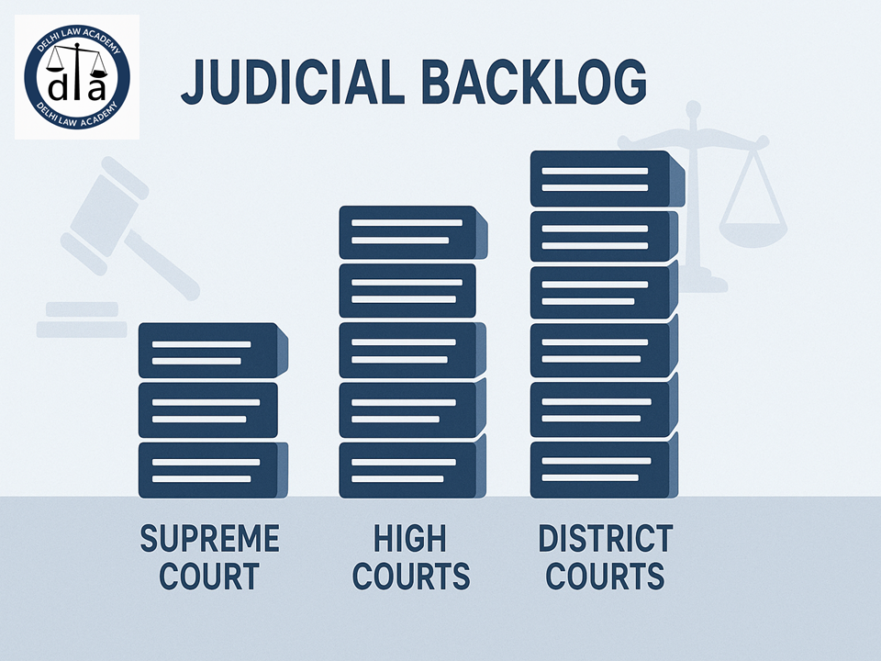
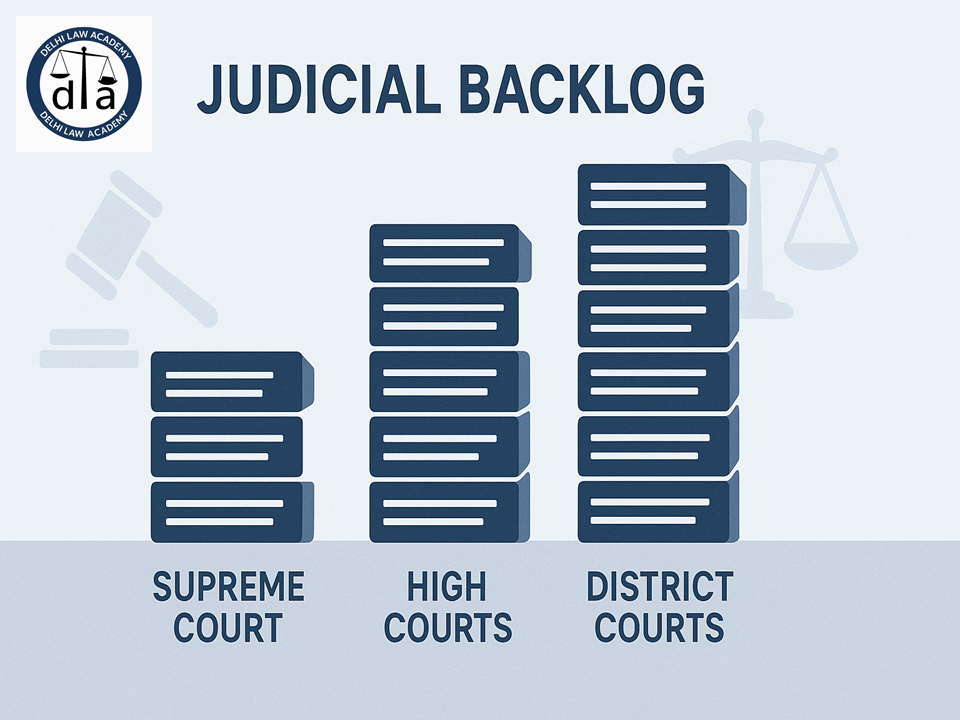
India’s judicial backlog has reached alarming levels — the Supreme Court alone has a record 88,417 pending cases, while High Courts face nearly 63 lakh cases and District Courts struggle under a staggering 4.6 crore cases (as per the National Judicial Data Grid 📊).
📈 Reasons Behind Judicial Pendency in India
- 👨⚖️ Inadequate Judge-to-Population Ratio: India has only 21 judges per million people — far below the 120th Law Commission recommendation of 50 judges per million.
- 🤝 Weak Implementation of ADR: Alternate Dispute Resolution mechanisms, including Gram Nyayalayas, remain underutilized in many states, failing to reduce court burdens.
- ⚙️ Systemic & Procedural Inefficiencies: Multiple appeals, adjournments, and frivolous litigation delay justice. Cases are rarely grouped or prioritized by urgency.
- 🏛️ Poor Judicial Infrastructure: Lack of staff, basic amenities, and digital tools in lower courts impede timely case management.
- 💰 Financial Constraints: India allocates only 0.1% of GDP to the judiciary — starkly low compared to other national priorities like defense (2%).
- 📑 Government as the Largest Litigant: Government departments contribute to nearly 50% of total litigation, clogging the system.
⚠️ Impact of Case Backlog on India’s Justice System
1️⃣ Violation of Fundamental Rights
In Hussainara Khatoon vs State of Bihar (1979), the Supreme Court held that the right to a speedy trial is part of Article 21 – Right to Life and Liberty. Case delays, therefore, constitute a constitutional violation.
2️⃣ Social Consequences
- ⚖️ Weakening Rule of Law: Criminal delay emboldens offenders and erodes deterrence.
- 🚔 Impact on the Poor: About 76% of prisoners are undertrials — incarcerated without conviction due to slow trials.
3️⃣ Economic Impact
- 💸 Rising Litigation Costs: Frequent adjournments increase lawyer fees and prolong cases.
- 🏗️ Stalled Infrastructure Projects: Delays in land and environmental cases block development and investments.
4️⃣ Loss of Public Trust
When justice is delayed, people lose confidence in the judiciary and turn to extra-legal methods — a phenomenon sometimes called the “Black Coat Syndrome” ⚖️🕰️.
💡 The Way Forward: Judicial Reforms Needed
- ⚙️ Digital Case Management: Use AI and data analytics for cause-list automation, case clustering, and real-time tracking.
- 👨💻 Strengthening e-Courts & Infrastructure: Expand virtual courts and video hearings beyond metros.
- 👩⚖️ Increasing Judge Strength: Recruit and train more judges at all levels for quicker case disposal.
- 🤝 Effective ADR Implementation: Strengthen Lok Adalats, Mediation, and Arbitration systems to resolve minor disputes faster.
🔚 Conclusion
The pendency of cases in India isn’t just a number — it’s a reflection of systemic inefficiency and public hardship. Addressing judicial delays requires technological modernization, administrative efficiency, and stronger institutional will.
Justice delayed is indeed justice denied. ⏳⚖️
📘 Free Study Material for Law Students!
Download our FREE study material prepared by Delhi Law Academy’s expert faculty.
Contact us
📍 Delhi Law Academy – Jaipur Branch
6C, Tower 2, Coaching Hub, Pratap Nagar, Jaipur – 302033
📞 Phone:
+91 9911916552
+91 8447285606
✉️ Email:
contactus@delhilawacademy.com