Introduction
Government Schemes in India can be classified into following major types:
1. Centrally Sponsored Schemes
(Funded both by Centre & States)
Currently, there are 29 centrally sponsored schemes. These are divided into two broad categories:
• Core of the core schemes – 6 Schemes
• Core schemes – 24 Schemes
• Other Schemes
2. Central Sector Schemes
(Funded & executed directly by Centre)
• These are second type of central welfare schemes being funded & implemented by centre directly. The different Union Ministries & departments are the executing agencies in these schemes.
3. State Government Schemes
(Funded & executed solely by States)
• These schemes are planned, funded & executed by the respective State Governments.
Difference between Centrally Sponsored Scheme & Central Sector Schemes
• The central welfare schemes at the state level fall into two broad categories. The first category is centrally sponsored schemes, and the second is the central sector schemes.
List of Centrally Sponsored Schemes in Union Budget 2020-21:
Core of the core schemes:
The six core of the core schemes are:
• National Social Assistance Programme
• MGNREGA or the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act
• Umbrella Scheme for Development of Scheduled Castes
• Umbrella Programme for Development of Scheduled Tribes
• Umbrella Scheme for Development of Minorities
• Umbrella Scheme for Development of Other Vulnerable Groups
Core Schemes:
There are 23 other centrally sponsored schemes, which are listed under core schemes. Most of the flagship schemes of the Union government are covered under this category. The centrally sponsored core schemes are:
• Green Revolution
• White Revolution
• Blue Revolution
• Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchai Yojna (PMKSY)
• Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojna
• Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojna (PMAY)
• Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM) / National Rural Drinking Water Mission
• Swachch Bharat Mission – Urban (SBM – Urban)
• Swachch Bharat Mission – Rural (SBM – Rural)
• National Education Mission
• National Health Mission
• National Program Mid-Day meal in schools
• Umbrella ICDS
• National Mission for Protection and Empowerment of Women
• National Livelihood Mission – Ajeevika
• Jobs & Skill Development
• Environment Forestry and Wildlife
• Urban Rejuvenation Mission: AMRUT and Smart Cities Mission
• Modernisation of Police Forces
• Infrastructure Facilities for Judiciary
• Border Area Development Programme
• Shyama Prasad Mukherjee Rurban Mission
• Rashtriya Gram Swaraj Abhiyan (RGSA)
• Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (including RSBY)
Others:
• National River Conservation Plan – Other Basins
• Credit Linked Capital Subsidy and Technology Upgradation Scheme (CLCS-TUS)
• Procurement and Marketing Support Scheme (PMS)
• Promotional Services Institutions and Programme – States
• Fortification of Rice and its Distribution under Public Distribution System
• Actual Recoveries
Agriculture & Allied Sector
Agriculture and allied sector activities primarily refers to cultivation of Crops, Animal Husbandry, Fisheries and Forestry.
Agriculture Related
Green Revolution- Krishonnati Yojana
It is an Umbrella Scheme comprising both Central Sector as well as Centrally Sponsored Schemes / Missions.
Objective: Developing the agriculture and allied sector in a holistic and scientific manner. Components: The 12 Schemes that are part of the Umbrella Schemes are –
• Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH);
• National Mission on Oil Seeds and Oil Palm (NMOOP);
• National Food Security Mission (NFSM);
• National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA);
• Sub-Mission on Agriculture Extension (SMAE);
• Sub-Mission on Seeds & Planting Material (SMSP);
• Sub-Mission on Agricultural Mechanisation (SMAM);
• Sub-Mission on Plant Protection and Plant Quarantine (SMPPQ);
• Integrated Scheme on Agricultural Census, Economics and Statistics;
• Integrated Scheme on Agricultural Cooperation;
• Integrated Scheme on Agricultural Marketing (ISAM);
• National e-Governance Plan in Agriculture (NeGP-A).
• National Food Security Mission (NFSM)
National Food Security Mission (NFSM)
• National Food Security Mission on Wheat and Pulses was launched in Rajasthan in the year 2007-08 as a centrally sponsored scheme by the Central Government.
• During the year 2015-16, Gol has changed the funding pattern and now Gol: GoR ratio is 60:40.
Components in Rajasthan:
• NFSM Pulses
• NFSM Wheat
• NFSM Coarse Cereals
• Nutri Cereals Bajra
• Nutri Cereals JOWAR
• Commercial Crops Cotton
Salient Features:
• The major interventions of NFSM-Wheat and Pulses relates to distribution of certified seeds, demonstration on improved production technology, support to farmers by providing bio-fertilizers, micronutrients and gypsum, Integrated Pest Management (IPM), agricultural implements, sprinklers, pump sets, pipe line for carrying irrigation water and cropping system based training.
• NFSM-Nutri-Cereals mission was launched in Rajasthan in 2018-19 as a Centrally Sponsored Scheme.
• The Major interventions in NFSM Nutri-Cereals relates to distribution of certified seeds, production of certified seed, demonstration on improved production technology, support to bio-fertilizer, micronutrients, integrated Pest Management (IPM) and cropping system based training for farmers.
• NFSM-Commercial Crops: Front line demonstration and distribution of plant protection chemicals for cotton crop.
• NFSM Oil seed & TBOS: Main Components of this mission are production of foundation seeds and certified seeds, distribution of certified seeds, crop demonstration, Integrated Pest Management (IPM), plant protection from chemicals, distribution of PP equipment, biofertilizer, Gypsum, pipes for carrying water, farmers’ trainings, agriculture implements, innovative seed treatment drums, sprinkler set, distribution of mini-kits, infrastructure development etc. Funding pattern between Gol and GoR is 60:40.
National Mission On Agriculture Extension and Technology (NMAET)
The aim of the Mission is to restructure & strengthen agricultural extension to enable delivery of appropriate technology and improved agronomic practices to the farmers. During the year 2015-16, Gol has reduced the funding pattern between Gol and GoR to 60:40. NMAET consist on 5 sub-missions:
• Sub Mission on Agriculture Extension (SMAE)
• Sub-Mission on Seed and Planting Material (SMSP)
• Sub Mission on Agriculture Mechanization (SMAM)
• National e-governance plan in agriculture
National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA)
• NMSA is one of the restructured schemes subsuming National Mission on Micro Irrigation, National Project on Organic Farming, National Project on Management of Soil health & Fertility and Rainfed Area Development Programme to focus on Climate change adaptation, being implemented since the year 2014-15.
• Share of Center: State in funding is 60: 40 percent.
National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA) consists of 4 sub missions:
• Rainfed Area Development (RAD)
• Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY)
• Soil Health Management and soil health card
• Sub-Mission on Agro-forestry
Rain-fed Area Development (RAD):
• Different types of area-specific Integrated Farming Systems (IFS) have been envisaged in different agro-climatic zones of the State i.e. Livestock based, horticulture based and agro¬forestry (Tree) based farming systems.
• Assistance is being provided for various IFS activities and allied activities.
• The farming systems are being taken up along with other activities like establishment of vermi compost units, construction of water harvesting structures and green houses, and beekeeping.
Soil Health Card Scheme (“Swasth Dhara Khet Hara”):
• The scheme envisages promoting the soil testing services, issue of soil health cards and development of judicious nutrient management practices for different crops.
Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY):
• Organic agriculture is production of agricultural products free from chemicals and pesticide residues, by adopting eco-friendly low cost technologies.
• Under PKVY, organic farming is promoted through adoption of organic village by cluster approach and Participatory Guarantee Systems (PGS) certification.
• Participatory Guarantee System under PGS-India programme is the key approach for quality assurance under the PKVY. The farmers have options to adopt any form of organic farming in compliance with PGS-India standards.
Sub-Mission on Agro-forestry (SMAF):
• SubMission on Agro-Forestry was launched in 2017-18 with the objective to encourage and expanding tree plantation in agriculture, ensuring availability of quality planting material and popularizing various Agro-Forestry Practices and models for different agro climatic zones and land use conditions and to creating database and knowledge support in the area of agro¬forestry.
Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY/ National Agriculture Development Programme)
• Government of India started RKVY during 11th five year to achieve the 4 per cent growth rate in Agriculture and allied sector.
• The scheme aims to draw up plans for agriculture sector more comprehensively, taking into account agro-climatic conditions, natural resource issues and technology.
• In this scheme project based assistance is provided to prepare Integrated District Agriculture plan in the field of Agriculture, Animal Husbandry, Fisheries, Poultry, Horticulture and Dairy, considering the agro-climatic conditions and natural resources of the State.
• During the year 2015-16, Gol has reduced the funding pattern to 60:40 (Gol: GoR).
Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchai Yojana (PMKSY)
• PMKSY has been conceived as an amalgamation of ongoing schemes viz. Accelerated Irrigation Benefit Programme (AIBP), Integrated Watershed Management Programme (IWMP) and the On Farm Water Management (OFWM).
• PMKSY is being implemented in the state, since 2015-16. PMKSY funding pattern between Gol: GoR is 60:40.
• Horticulture department is the Nodal department and different activities are being implemented by Agriculture, Horticulture, Watershed development & soil conservation and Water Resource department.
Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY)
• PMFBY was restructured by the Weather Based Crop Insurance Scheme (WBCIS) and modified National Agriculture Insurance Scheme (NAIS) during the year 2016-17.
• This scheme has been implemented since kharif crops 2016.
• The scheme covers food grain crops (cereals, millets and pulses), oilseeds and Annual Commercial/Annual Horticultural crops.
• The farmer premium for Kharif crops, Rabi crops and Annual Commercial/Annual Horticulture crops is 2 per cent, 1.5 per cent and 5 per cent respectively. The Central and State Government pay remaining part of the premium equally in the ratio of 50:50.
• For payment of premium subsidy and incentive to primary workers for conducting crop-cutting experiments, a state funded scheme is in operation.
Krishi Karman Awards
• The Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, Government of India has given Karman Award Krishi Karman Award for the year 2016-17, for outstanding performance in the pulses production category.
• 2.00 crore, citation and trophy given as Krishi Karman Award.
• Additionally, two progressive farmers of the state, one male and one female farmer were given each *2 lakh and citation.
• The state also received a commendation award of 31.00 crore in the pulses category for the year 2017-18 on 2 January, 2020.
Zero Budget Natural Farming:
• In compliance of Budget Announcement 2019-20 made by Hon’ble Chief Minister, a pilot project on Zero Budget Natural Farming is being implemented in Tonk, Banswara and Sirohi districts of the state.
• This will eventually make the farmers self-sustainable through the use of agri-inputs prepared by themselves in-farm and reduce the cost of cultivation, it would also allow them to grow chemical free agriculture produce.
Rajasthan Agricultural Competitiveness Project (RACP):
• With the objective to increase production and productivity, farmer’s income, promote climate resilient agriculture, reduce water use in agriculture, and involve farmers in processing and value addition, RACP is being implemented in 17 clusters of 17 districts of the state with credit from World Bank.
• Besides, establishment/ operating expenses of field staff/labs/Kisan Aayog/ capital works, Kisan Seva Kendra cum village knowledge centre, Information and Media support, Computerization and State Matching Share towards Central Sponsored Schemes have also been included in the State Plan.
THAR Scheme
• The State Government in planning to bring Transforming and Harvesting agriculture and allied sector in Rajasthan scheme – Thar scheme for new investment in agriculture sector.
• The scheme will aim at reducing the cost of farming, increasing the income of farmers, encouraging agricultural processing, promoting information technology in agriculture and bringing the agriculture and related products of the state to the markets of the country and the world under Rajasthan. Innovations will be involved.
Horticulture
Recent initiatives include:
• Vegetable cluster in urban areas,
• Establishment of Centers of Excellence at Jhalawar, Dholpur, Tonk, Bundi, Chittorgarh and Sawai Madhopur
• Centre of excellence of pomegranate, Bassi (Jaipur) and Citrus Nanta (Kota)
Operation Greens Scheme (TOP to TOTAL)
Ministry is implementing a central sector scheme, namely “Operation Greens Scheme” – A scheme for integrated development of Tomato, Onion and Potato (TOP) value chain with a budgetary allocation of Rs. 500 crores. The scheme has two-pronged strategy of Price stabilisation measures (for short term) and Integrated value chain development projects (for long term).
Due to restriction imposed on account of COVID-19, the supply chain has been disrupted and famers are not able to sell their produce in the market. To improve this situation, Ministry of Food Processing Industries (MoFPI) has recently extended the Operation Greens Scheme from Tomato, Onion and Potato (TOP) to all fruits & vegetables (TOTAL) for a period of six months on pilot basis as part of Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan.
Salient Features of Operation Greens Scheme (Total)
Objective:
• The objective of intervention is to protect the growers of fruits and vegetables from making distress sale due to lockdown and reduce the post – harvest losses.
Eligible Crops:
• Fruits- Mango, Banana, Guava, Kiwi, Lichi, Papaya, Citrus, Pineapple, Pomegranate, Jackfruit;
• Vegetables – French beans, Bitter Gourd, Brinjal, Capsicum, Carrot, Cauliflower, Chillies (Green), Okra, Onion, Potato and Tomato.
• Any other fruit/ vegetable can be added in future on the basis of recommendation by Ministry of Agriculture or State Government
• Fist of eligible crops, selected surplus production clusters and trigger price for intervention under the scheme
Eligible Entities:
• Food Processors, FPO/FPC, Co-operative Societies, Individual farmers, Licensed Commission Agent, Exporters, State Marketing/Co- operative Federation, Retailers etc. engaged in processing / marketing of fruits and vegetables.
National Horticulture Mission (NHM)
• To increase the area, production and productivity of different horticulture crops like fruits, spices and flowers in selected 24 districts namely Jaipur, Ajmer, Alwar, Chittorgarh, Kota, Bar an, Jhalawar, Jodhpur, Pali, Jalore, Barmer, Nagaur, Banswara, Tonk, Karauli, Sawai Madhopur, Udaipur, Dungarpur, Bhilwara, Bundi, Jhunjhunu, Sirohi, Jaisalmer and Sri-Ganganagar.
• Activities include establishing fruit orchards, providing green-houses, plastic tunnels, plastic mulching, vermin-compost units, low cost onion storage units, pack-houses and water harvesting structures etc.
Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchai Yojana – Micro Irrigation (PMKSY-MI)
• Additionally, during 2015-16, Government of India launched Micro Irrigation Scheme under PMKSY.
• The ratio of central share and state share for all categories of the farmers is 60:40.
• Activities include promoting efficient water management practices (like drip & sprinkler irrigation) to improve crop yields & quality along with water-saving.
Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY)
Under this scheme activities include
• Date palm cultivation, horticulture development programme in non NHM districts,
• Vegetable cluster in urban areas,
• Establishment of Centers of Excellence at Jhalawar, Dholpur, Tonk, Bundi, Chittorgarh and Sawai – Madhopur,
• Strengthening of center of excellence of pomegranate in Bassi (Jaipur) and Nanta (Kota),
• Promotion of protected cultivation; skill up-gradation in citrus production.
National Agro-Forestry and Bamboo Mission (NABM)
Under this scheme, the districts of Karauli, Sawai-Madhopur, Udaipur, Chittorgarh, Banswara, Dungarpur, Sirohi, Baran, Jhalawar, Bhilwara, Rajasmand and Pratapgarh were taken up for promoting bamboo cultivation.
National Mission of Medicinal Plants
National Mission of Medicinal Plants aims at promoting cultivation of medicinal plants, raw materials to pharmacy sector could easily be made available in sufficient quantity. Ayush Department of Rajasthan is the nodal agency for implementing the scheme.
PM – Kisan Scheme
The PM-KISAN scheme was launched in December 2018 to provide income support by way of a cash benefit to all landholding farmers (subject to certain exclusion criteria) to enable them to fulfil their agricultural requirements and support their families.
Under the scheme, the financial benefit of Rs.6000/- per year is provided to eligible beneficiary farmers in three equal instalments.
On 9th August 2020, the 6th instalment under the PM-KISAN scheme of Rs. 17,000 Crore was paid to nearly 8.5 Crore farmers. The cash benefit was transferred directly to their Aadhaar verified bank accounts.
With this transfer, the scheme has provided over 90,000 Crore in the hands of more than 10 Crore farmers since its launch on 01 December 2018.
Agricultural Marketing
Rajeev Gandhi Krishak Sathi Sahayata Yojana
• Rajeev Gandhi Krishak Sathi Sahayata Yojana provides financial assistance for agriculture marketing to agriculturist, agricultural labourer and hamals.
• Under this scheme, financial assistance have been provided to the tune of 2 lakh in the case of work-site accidental death.
Kisan Kaleva Yojana
• Kisan Kaleva Yojana has been introduced for farmers to provide them quality food on subsidized rates in ‘Super’, ‘A’ and ‘B’ class krishi upaj mandi samities of the State.
Mahatma Jyotiba Phoole Mandi Sharmik Kalyan Yojana 2015
Mahatma Jyotiba Phoole Mandi Sharmik Kalyan Yojana 2015 has been launched in the State. Important features of the scheme are:
• Pregnancy assistance of rupees equivalent to 45 days non-skilled labour rate is being provided to license holder lady labourer for two pregnancy period.
• Marriage Assistance: Licensed lady labourer will be entitled for a sum of ‘20,000 for marriage of her girl. This assistance is limited for marriage of upto 2 girls only.
• Scholarship: The son/daughter of licensed labourer obtaining 60 per cent or above marks is entitled for scholarship under this scheme.
• Medical Assistance: Financial assistance of ‘20,000 will be given to licensed labourer in case of serious disease.
• Parental Leave:
Krishi Kalyan Kosh
Taking the first major step towards ’Ease of Doing Farming’ on the lines of ’Ease of Doing Business’ in the Rajasthan Budget 2019-20, the formation of a farmers welfare fund named as Krishi Kalyan Kosh (K3) was announced by the Chief Minister.
This fund will be used to provide the farmers with fair prices for their produce. Its budget has been kept at 1 thousand crores.
Animal Husbandry
Initiatives during 2019-20:
• Under the mandate of Foot and Mouth Diseases (FMD), free Rajasthan FMD-CP is being implemented in the State with the assistance of Government of India. Mass Vaccination Campaigns are going on in the State for cattle and buffalo twice a year.
• Livestock Breeders are being benefited under Pashudhan Nishulak Arogya Yojna regularly.
• Breed improvement program has also been strengthened.
• Training facility for livestock farmers has been improved and extended.
• Under the National Livestock Mission, genetic improvement of Goat and Sheep (GIGS) scheme has been started with the assistance of Gol: GoR with the 60:40 funding pattern. Under the scheme exhibition and training camps are organized for selection of male and female goats with preferred genetic characters. Presently the scheme is being run in Ajmer, Jaipur, Sikar, Rajsamand, Chittorgarh, Churu, Sirohi and Kuchaman City (Nagour) Districts.
• Under the National Livestock Mission, Innovative Poultry Productivity Project (IPPP) has been started for Poultry Farmers. Under this project IPPP for Broiler and LIT Birds projects has been included.
• Establishment of 400 new veterinary sub centres have been proposed in the year 2019-20 in those gram panchayats where departmental veterinary facility is not available. Out of these, 226 new sub centres have been opened upto December, 2019.
Gopalan Department
Some Important Schemes:
• Nandi Goshala Jan Sahbhagita Yojana
• Gau Abhyaranya Yojana
Dairy Development
The Dairy Development Programme in Rajasthan is being implemented through Cooperative Societies. Under this Programme, 15,017 Dairy Cooperative Societies have been affiliated with 21 District Milk Producers Cooperative Unions spread over the State and a State level Apex Body, ‘Rajasthan Cooperative Dairy Federation (RCDF) Limited, Jaipur is functional.
Some Important Schemes:
• Saras Surksha Kavach’ (Janshree),
• Raj Saras Surksha Kavach Bima Yojana’ (Accidental),
• Saran Samuhik Arogya Bima
• Chief Minister Dugdh Utpadak Sambal Yojana Fisheries related Schemes
The State Department has started implementation of ambitious scheme on ‘livelihood model’, which is a ‘zero revenue’ model, for the upliftment of tribal fishermen in three reservoirs namely Jaisamand (Udaipur), Mahi Bajaj Sagar (Banswara) and Kadana Backwater (Dungarpur).
• As per the new model, the lift contract has been given to the highest bidder. One of the important conditions is to transfer whole fish catch price to tribal fisherman and these fish catching rates are highest in the country.
• A total of about 7,193 fishermen of 56 fishermen cooperative societies are being benefitted under this model and the earning of tribal fishermen working on regular basis has increased manifold.
National Mission for Protein Supplement
• Under National Mission for Protein Supplement scheme, a cage culture project has been sanctioned by Government of India at a cost of 3.44 crore for the dissemination and demonstration of modern fisheries-techniques at Mahi Bajaj Sagar (Banswara) and 56 cages have already been installed there.
• 3.64 crore has been sanctioned for Ornamental Fish breeding unit and aquarium gallery and it is under construction as an innovative work at Bisalpur Dam (Tonk).
Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY)
• Under Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY), an amount of ‘15.30 crore has been approved for the modernization/ construction of 41 fish landing centres of Rajasthan to reduce the post-harvest losses.
• The construction of fish landing centres at Ramsagar (Dholpur), Bisalpur (Tonk) and Rana Pratap Sager (Rawatbhata) have been completed.
• Construction of landing centres at Jawaidam (Pali) and Jaisamand (Udaipur) has been completed and working at present.
Jan Aaushadhi Kendra
• 200 Jan Aaushadhi Kendra will be established by CONFED under Pradhan Mantri Jan Aaushadhi project. Presently Jan Aaushadhi Kendras are being operated in Udaipur, Jodhpur, Jhunjhunu and Dungarpur by Districts wholesale consumer stores and in Jaipur by CONFED. One Jan Aaushadhi Kendra is being operated by CONFED at SMS hospital Jaipur and one medicine selling centre is also being opertaed in Santokba Durlabhji Memorial Hospital (SDMH) Jaipur.
Employment & Livelihood
Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME)
Stand Up India Scheme
• Stand up India scheme was envisaged for promoting entrepreneurship among SC/ST and women entrepreneurs. The overall intent of scheme is to leverage institutional credit structure to reach out to the underserved of the population by facilitating bank loans between 10 lakh and 21 crore which is repayable in upto 7 years for green field enterprises in non-farm sector set up by SC / STS and women entrepreneurs.
• To facilitate operation under the scheme Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI) has set up a web-portal (http:/ / www.standupmitra.in) with a view to promote wider propagation of the scheme and address any queries.
Mukhyamantri Laghu Udyog Protsahan Yojana (MLUPY):
• For setting up new enterprises in the manufacturing, service and trade sectors and for expansion, modernization, diversification of existing enterprises to provide loans upto 10 crore through financial institutions, “Mukhyamantri Laghu Udyog Protsahan Yojana” has been notified and has been commenced from 13h December, 2019.
• Under the scheme, small scale entrepreneurs will be provided 8 per cent interest subsidy on loans upto 25 lakh, 6 per cent on loans upto 5 crore, 5 per cent on loans upto 10 crore.
Export Promotion Initiatives:
State Level Exports Award Scheme:
• The scheme was declared in the Industrial Policy, 1994 with the objective of encouraging exporters of the State. There is provision for selection of 31 outstanding exporters in 16 categories. Under this,
• 1 best exporter per year in the State will also be awarded with “Lifetime Achievement Export Ratna Award”.
Export Promotion Council
• To encourage export in the State “Rajasthan Export Promotion Council” (8″ November, 2019) and “Rajasthan Export Promotion Coordination Council” (25 October, 2019) were formed.
Ease of Doing Business
• The State Government has continuously pursued rationalizing the regulatory process for establishing businesses and industrial units across departments. To improve the Ease of Doing Business, State is following and implementing the yearly Business Reforms Action Plans (BRAP) of Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) Government of India.
Rajasthan Investment Promotion Scheme 2019
• The State Government of Rajasthan, has in 2019 issued “The Rajasthan Investment Promotion Scheme, 2019” (RIPS-2019) to provide benefits to eligible manufacturing and services sector enterprises. Additionally, the scheme also aims to generate employment opportunities and promote rapid, sustainable and balanced economic growth in Rajasthan.
• The Scheme Rajasthan Investment Promotion Scheme, 2019 (RIPS 2019) has come into effect from 17 December 2019 and shall remain in force up to 31st March 2026.
Salient Features of Rajasthan Investment Promotion Scheme, 2019 (RIPS-2019)
Industry 4.0
• RIPS 2019 defines Industry 4.0 as the enterprises engaged in big data & analytics, artificial intelligence, nano technology, quantum computing, fifth-generation wireless technologies, simulations, horizontal & vertical system integration, cyber security, cloud, additive manufacturing and augmented reality across the business value chain.
Investment not eligible for benefits of subsidies/ exemptions under RIPS 2019
• Investment for manufacturing tobacco, tobacco products and pan masala.
• Investment made in cow beef processing units.
• Investment made in retail / trading activities.
• Any activity which is prohibited by Central / State laws.
Prime Minister Employment Generation Programme (PMEGP)
• Prime Minister’s Employment Generation Programme (PMEGP) is a credit linked subsidy programme administered by the Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises, Government of India.
• Khadi & Village Industries Commission (KVIC), is the nodal agency at national level for implementation of the scheme. At state level the scheme is implemented through KVIC, KVIB and District Industries Centre.
• This scheme aims to generate employment opportunities by promoting industrial service and manufacturing activities in rural and urban areas of the state.
Rajasthan Unemployment Allowance Scheme (Mukhaymantri Yuva Sambal Yojana)
• State Govt, started providing unemployment allowance from 1* February 2019.
• The State Government has revised the earlier unemployment allowance to ^3,000 per month for men and ^3,500 per month for women and specially abled persons.
• For upto 2 years or till one gets employment, whichever is earlier.
• As of December 2019 – 1,59,728 beneficiaries.
Mukhya Mantri Yuva Kaushal Yojana (MMYKY)
• The Mukhya Mantri Yuva Kaushal Yojana (MMYKY), launched on 7 November, 2019, endeavors to integrate Skill Development in academic colleges. Skill Development Centers located within college premises are offering domain and Life Skills/ Soft Skills courses to improve employability of College student of graduation level.
• The objective of this program is to provide employability skills through a combination of soft skills and domain based skills to students across colleges so that after training they can avail wage or self- employment opportunities
• The scheme is being implemented in joint collaboration of RSLDC and College Education Department (Commissionerate of College Education, Rajasthan) and the batches are being conducted by training partners empaneled by RSLDC by using college premises of respective colleges.
• Under this scheme, 45 special courses have been prepared which are relevant to college youth. Courses are having maximum duration of 350 hours. In each domain course, 90 hours of soft skill component are incorporated. While the scheme is for college going youth which may opt further higher education (Master’s Degree or so), the scheme is exempted from placement norms.
• During first phase of this scheme RSLDC has allotted targets to train 6,000 youth. Age for the scheme is 17 to 30 years.
• RSLDC has forged the partnerships under flexi MoU scheme with the opportunity for industry to customise the course curriculum as per their industry demands and benefit the youth with exposure to industry environment and their 360 degree career development.
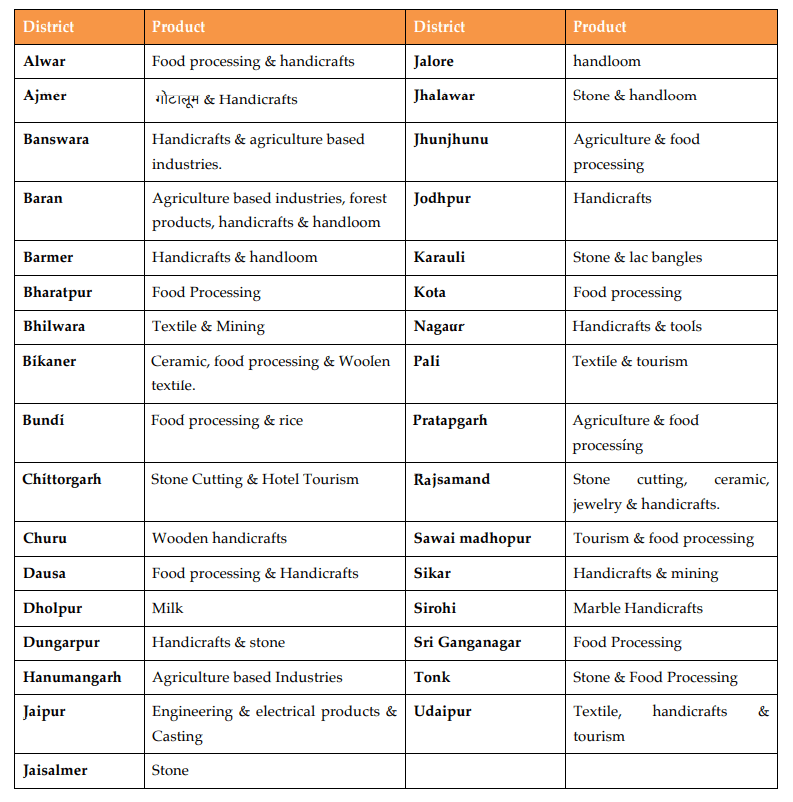
One District One Product Scheme
Since February-March 2020, Rajasthan Government has been working on one district one product scheme.
Finance Based
Rajasthan Jan Aadhaar Scheme
In December 2019, the State cabinet decided to replace Bhamashah card with Jan Aadhaar card from April 1, 2020. Consequently, the new Jan Aadhar Card was inaugurated on 18th December 2019.
‘One Number, One Card and One Identity’ – Jan Aadhaar Card – Tagline
Salient Features of Jan Aadhaar Card:
• 10 digit number
• All resident families in the State of Rajasthan, will be eligible to have the Jan Aadhaar Card
• The card will replace all other cards like aayushman card, ration card etc.
• Similar to Bhamashah card, would identify family, with Woman as head of family.
• Woman above the age of 18 years of the family will be considered as the head of the family. If there is no woman above 18 years of age in the family, in such a case, a man of 21 years or more will be made the head.
• In a family, if there is no female above 18 years of age and no man above 21 years of age, then any member of the family, having maximum age will be considered as the head of the family.
• Will provide benefits / services related to government / welfare schemes.
• Will be valid as proof of identity (Pol) and proof of address (PoA).
• Will be accessible through mobile and enable description of all available benefits.
Rajasthan Jan-Aadhaar Yojana
The main objectives of the scheme are
• To create a demographic and socio-economic database of the resident families of the state and to provide them “one number, one card and one identity” which can be recognised as Proof of Identity and Proof of Address for all the families and their members.
• To ensure direct benefit transfer (DBT), the cash benefits are to be transferred to the bank account to the beneficiaries and non-cash benefits are to be provided through Jan-Aadhaar or Aadhaar authentication
• To extend the facilities of e-commerce and insurance benefits near by door-step of the residents, especially in the rural areas, besides extending direct benefit transfer of public welfare schemes.
• To bring the e-Mitra system of the state under the jurisdiction of Rajasthan Jan- Authority for its better control and execution.
• To bring all the demographic registrations (viz. Birth, Death, Marriage, Aadhaar etc.) under the Rajasthan Jan-Aadhaar Authority for continuous updation of population status and maintaining a real-time census of the state.
• To promote women empowerment and financial inclusion To ascertain eligibility of residents of the state for receipt of the benefits and services of the public welfare schemes.
Implementation of the Scheme
• All the resident families of the state are eligible for Jan-Aadhaar Card.
• The registered families are going to be provided with a 10-digit unique family ID and each member of these families, including the head of the family, will be provided with 11-digit unique individual ID.
• Under Jan-Aadhaar Scheme, the benefit transfer of schemes such as PDS, MGNREGA, SSP, Ayushman Bharat Mahatma Gandhi Rajasthan Swasthya Bima Yojana, JSY etc. are being commenced.
E-Mitra
• E-Mitra is a multi-service, single-window network for providing governmental information and services to the citizens.
• Further, Mobile Wallets such as PayTM, and m-pesa have been integrated to provide mobile payment facility to the beneficiaries.
Business Correspondent
• Financial Inclusion is the process of ensuring access to financial services and timely and adequate credit to the needy and vulnerable groups such as weaker sections and low-income groups at an affordable cost, if any.
• Banks are providing banking services through brick and mortar branches, banking and business correspondents under financial inclusion in the state.
• Currently more than seventy thousand E-mitra Pay Points and 18,000 Business Correspondent (BCs) are working in the State.
Other Schemes:
• Under the scheme “Pradhan Mantri Jan-Dhan Yojana (PMJDY)” in Rajasthan 2.66 crore accounts have been opened and Aadhaar seeding of 86.18 per cent accounts have been completed upto 31″ December, 2019.
• In the State under the “Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bema Yojana (PMJJBY)”, a total of 22.06 lakh persons and under “Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana”, a total of 72.09 lakh persons have been enrolled upto 31″ December, 2019.
• Atal Pension Yojana (APY) is a pension scheme with focus on workers of the sector. The minimum age of joining APY is 18 years and maximum age is 40 years. Under the scheme, guaranteed minimum pension of 1,000 per month is given after attaining the age of 60 years contingent on contribution by the subscriber. In the state, under this scheme, total of 8,33 lakh persons have been enrolled upto 31″ December, 2019
• Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY) through banks, Non-Banking Financial Company (NBFC) – Micro Finance Institutions and Non-Banking Financial Companies in the Rajasthan.
Rural Development
Water Resources:
Rajiv Gandhi Jal Sanchay Yojna (RGJSY)
• Rajasthan, with a geographical area of 343 lakh hectare, is the largest State of the country, having 10.40 per cent of the total area of the country. Out of this area, about 101 lakh hectare is waste land and only 168 lakh hectare area is cultivable.
• Despite being the largest state in terms of area, only 1.16 per cent of total water resources is available in the state. The annual rainfall in the state also varies from 100 mm in the arid west to 900 mm in the South-East.
• Usually, every three out of five years, most districts of the state are affected by drought because of uncertain and varied distributions of rainfall. Moreover, owing to high intensity of rainfall and improper water conservation system, a large percentage of this rainfall goes waste resulting in continuous depletion of water table and further, conversion of cultivable land into waste-land.
• To resolve these serious issues, the State Government has decided to launch Rajiv Gandhi Jal Sanchay Yojna (RGJSY) to ensure maximum rainwater harvesting, water conservation and judicious use of available water sources in the State.
• Rajiv Gandhi Jal Sanchay Yojna (RGJSY) is being implemented with effective convergence of various Central and State schemes, effective convergence of funds, assistance of Corporate, Religious trusts, Social sects, NGOs and public contribution, and by providing State fund to execute water conservation and water harvesting activities.
Major Objectives of RGJSY:
• To generate awareness about water conservation.
• To ensure effective implementation of rejuvenation of traditional water resources, construction of new water sources, water conservation and water harvesting related activities in rural areas from available financial resources (Centre, State, Corporate, Trusts and People’s participation) through effective convergence.
• To make efforts to ensure availability of drinking water within village/ nearby village vicinity and resolve the issue of shortage of drinking water.
• To improve the status of ground water availability and to check the rate of depletion of water table.
• To increase cultivable area and irrigated area through water conservation and rain water harvesting activities.
• To increase green cover through intensive afforestation
Major Activities:
• Watershed (catchment) area treatment: Trenches, Farm Ponds, Mini Percolation Tank (MPT), Khadin, Johar, Tanka, Small Anicuts, Earthen check dams, Water harvesting structures, Field Bund, Water storage structures etc.
• Repair of minor irrigation work, renovation and reinforcement work.
• Reinforcement of drinking water sources.
• Construction of artificial recharge structures.
• Pasture development & plantation.
• Promotion of advanced methods of cropping & horticulture (Drip, Solar pump etc.).
Atal Bhujal Yojana
• On the birth anniversary of late Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee, PM Modi launched Atal Bhujal Yojana or Atal Jal Scheme, aimed at improving groundwater management through community participation in seven states.
• The scheme is aimed at contributing towards the goal of doubling farmers’ incomes, promoting participatory ground water management, improving water use efficiency on a mass scale, improving cropping pattern and promoting efficient and equitable use of ground water resources and behavioural change at the community level.
The Scheme will be implemented in identified 8,350 gram panchayats in 78 districts (priority areas) in seven states including –
• Gujarat
• Haryana
• Karnataka
• Madhya Pradesh
• Maharashtra
• Rajasthan
• Uttar Pradesh
The Scheme has two major components:
• One is institutional strengthening and capacity building for sustainable ground water management in the states including improving monitoring networks, capacity building, strengthening of water user associations.
• The second component is incentivising the states for achievements in improved groundwater management practices namely data dissemination, preparation of water security plans, implementation of management interventions through convergence of ongoing schemes, adopting demand side management practices, etc.
Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM) / National Rural Drinking Water Mission
Objectives:
• To provide piped water supply to all rural households by 2024.
• The mission envisages supply of 55 litres of water per person per day to every rural household by 2024.
• Also aims to create local infrastructure for rainwater harvesting, groundwater recharge and management of household waste water for reuse in agriculture.
Jal Jeevan Mission in Rajasthan
• A “mission mode” has been adopted in Rajasthan for providing piped water supply connections to about 98 lakh households stipulated in the flagship Central scheme. Only 12% of the households in the State were currently getting piped water supply, a huge task lay ahead to meet the target.
• Jal Jeevan Mission would be implemented under the State Water and Sanitation Mission, which was already functional. Water and Sanitation Committee and Water Committee would be set up in each of the districts.
Chief Minister Raj Neer Scheme
On 13th March 2020, Chief Minister of Rajasthan announced “Chief Minister Raj Neer Scheme” in the Vidhan Sabha.
• Water charges will be waived if the monthly water consumption of domestic consumers is less than 15 thousand litres in the urban area of the state.
• For this non-working water meters will be replaced with smart water meters.
• In the first phase, 10 lakh water meters will be replaced in the next 3 years in 29 cities with more than one lakh population.
• For this, a provision of Rs 25 crore is being made in the financial year 2020-21.
• Similarly, 55 TPCD free drinking water will be supplied to domestic consumers in rural areas and up to 70 TPCD water consumption will be waived in desert areas.
Rajasthan Grameen Aajeevika Vikas Parishad -RAJEEVIKA (RGAVP)
• RGAVP is an autonomous society established in October, 2010 by the Government of Rajasthan under the administrative control of Department of Rural Development.
• The society is registered under Society Registration Act, 1958 and is mandated to implement all rural livelihood programmes associated with Self Help Group (SHG) based institutional architecture.
• The objective of the RGAVP is to implement Self Help Groups (SHGs) based livelihood program, financial Inclusion through project fund and bank linkage in the State.
At present, following livelihood projects are being implemented by RAJEEVIKA:
• National Rural Economic Transformation Project (NRETP) is being implemented in 36 blocks in 9 districts.
• Government of India funded National Rural Livelihood Mission (NREM) is being implemented in 272 blocks in phased manner since April, 2013.
The key activities undertaken in the projects being implemented by RAJEEVIKA are as follows:
• Institution Building
• Capacity Building
• Financial Inclusion
• Livelihood Intervention
• Convergence
Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS)
• The programme aims to provide employment to rural people and thereby enhance inclusive growth and is operational in the entire state.
• The objective of the scheme is to enhance livelihood security in rural areas by providing at least 100 days of guaranteed wage employment in a financial year to every household whose adult members volunteer to do unskilled manual work.
Salient features of the scheme are as under:
• All local residents of the Gram Panchayat are eligible for registration under the Scheme.
• Minimum one third beneficiaries shall be women.
• Job Cards with photographs of all the adult members of the household are issued free of cost within 15 days of registration.
• Dated receipt of application for employment is provided.
• Guarantee of providing employment within 15 days of application.
• Un-employment allowance is paid by the State Government, if employment is not provided within 15 days of application.
• Work is provided within 5 Km. radius of the village. Beyond 5 KM, 10 per cent extra wages are payable.
• Wages are to be paid as per the task performed.- Drinking water, shade, first aid and creche facilities are mandatory at worksite.
• Gram Sabha is the primary authority to identify the works and to prepare annual action plan.
• No contractors and labour placing machinery is allowed.
• Social Audit by Gram Sabha.
• All wage payments through Banks/Post Offices only.
• Gram Sabha is empowered for monitoring the progress and the quality of work.
• Effective Grievance Redressal mechanism.
Pradhanmantri Awas Yojana – Gramin
The scheme of Indira Awas Yojana (IAY) has been restructured into Pradhanmantri Awas Yojana – Gramin-(PMAY-G). The scheme was launched by Prime Minister on 20th November, 2016.
Features:
• Selection of beneficiaries under the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana – Gramin will be done on the basis of Socio Economic Caste Census-2011 (SECC-2011) data.
• The government provides a financial assistance of Rs. 1,20,000 to the beneficiaries.
• Along with this, an additional Rs. 12,000 will also be provided to build toilet to each under the Swachch Bharat Mission.
• The beneficiaries are also be provided daily wages upto 90 days through MGNREGA.
• The expenditure is shared is in the ratio of 60:40 between Central and State Government.
Mewat Area Development Programme
• The area inhabited by Mev’s is known as Mewat area. The Mev community is concentrated in 12 blocks of Alwar and Bharatpur Districts.
• The Mev are still socially and economically backward and hence, Rajasthan Government is running a special development program since 1987-88 for overall development of Mewat area.
Border Area Development Programme (BADP)
• The Border Area Development Programme (BADP) was introduced during the 7th Five Year Plan as a Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS). The BADP is a Central Government intervention strategy to bring about a balanced development of border areas.
• The programme is being implemented in 16 Blocks of 4 Border Districts, namely Barmer, Bikaner, Ganganagar and Jaisalmer. Under BADP, majority of the funds are invested for security related activities. However, since the border districts have poor social and economic infrastructure development activities are also provided due importance.
Dang Area Development Programme
• Dang Area Development Programme has been re-launched in 2004-05 by Government of Rajasthan. The Programme covers 394 Gram Panchayats of 26 Panchayat Samities of 8 Districts (Sawai Madhopur, Karauli, Dholpur, Baran, Jhalawar, Bharatpur, Kota and Bundi).
Magra Area Development Programme
• The central Southern part of Rajasthan surrounded by hills specially Ajmer, Bhilwara, Pali, Chittorgarh and Rajsamand and not covered under Tribal Area Development (TAD) is locally known as “Magra“
• To improve social and economic status of residents, the “Magra Area Development Programme” was initiated since 2005-06 in 14 Blocks of above 5 districts. At present it is being implemented in 16 blocks in above districts.
• Activities of Watershed Development, Minor Irrigation, Animal Husbandry, Drinking Water, Education, Electrification, Health and Road Construction are undertaken for development of the area.
Bio Fuel Mission & Authority:
• The Bio fuel mission was formed to enable production of Bio Fuel on cultivable wasteland as well as on degraded forest land of Rajasthan through Jatropha, Karanj and other such tree borne oil seeds.
• Rajasthan is one of the fastest developing states in the country and is privileged to become the first state to develop Bio-fuel Policy in the year 2007 and its implementation in the field.
• 12 districts of Rajasthan namely Baran, Banswara, Bhilwara, Bundi, Chittorgarh, Dungarpur, Jhalawar, Kota, Rajsamand, Sirohi, Udaipur & Pratapgarh are found suitable for plantation of Jatropha and 8 districts of Eastern Rajasthan namely Alwar, Bharatpur, Dausa, Dholpur, Jaipur, Karauli, Sawaimadhopur & Ton are found suitable for Karanj.
• Rajasthan Wasteland Development Board has been reconstituted as Wasteland & Pasture Development Board on 22 December 2016 with objectives to develop wasteland and pastures of the state.
Saansad Adarsh Gram Yojana (SAGY)
• The main objectives of SAGY are to trigger the processes, which lead to holistic development of the identified Gram Panchayats, to substantially improve the standard of living and quality of life of all sections of the population and instilling certain values in the villages and their people, so that they get transformed into models for others.
• In the first phase, 34 gram panchayats have been selected by the hon’ble MP’s.
Mahatma Gandhi Adarsh Gram Yojna
• On the occasion of the 150 birth anniversary (year 2019) of the Father of the Nation “Mahatma Gandhi Adarsh Gram Yojana” was launched on 27″ November, 2019. Under this scheme, one village in each district is to be selected and developed according to Gandhian values.
• The main activities of the scheme covers family welfare programs for population control, cooperation in national programs for the nutrition and health of pregnant and lactating women, attention to children’s health screening and vaccination, establishment of drug-free society and organising education and skill training programs.
• The works to be undertaken in this scheme also include conservation of all natural resources, historical heritage, cultural heritage, religious sites, cremation, burial grounds, protection of sustainable social, cultural and economic development, housing and toilets etc.
• The scheme proposes to organise Independence Day, Mahatma Gandhi Jayanti and Republic Day every year to develop an atmosphere of goodwill.
Smart Village
• The Chief Minister of Rajasthan in the Budget 2017-18 announced Smart Village scheme. In this scheme, 3,275 Villages are selected to develop as a SMART VITTAGE., which includes development of the village with modern amenities like a city and its funds are being provided by various departmental schemes.
• Activities like Drainage system & pucca streets, Community toilets, Public park / play grounds with open gym, Charagah land development and fodder production, Solar or TED lights in streets, develop one road as SwaRaj Marg, developing senior secondary school, primary/sub health centre, Veterinary hospital, Mil production samiti, Clean drinking water facilities, Food grain storage, blouse under PMAY-G to all beneficiaries.
Swachh Bharat Mission (Rural)
Prime Minister of India launched the program on 2nd October, 2014 with aim to make the country Open Defecation Free (ODF) by 2nd October, 2019. Rajasthan has achieved ODF status by March, 2018.
Incentives:
• Incentive for construction and usage of Individual Household Latrines (IHHL) shall be available for all Below Poverty Line (BPL) Households and Above Poverty Line (APL) households restricted to SCs/STs, small and marginal farmers, landless labourers with homestead , physically handicapped and women headed households.
• The Incentive amount provided to Below Poverty Line and identified Above Poverty Line households is upto ‘12,000 for construction and usage of one unit of Individual Plousehold Latrine (IHHL). Central Share of this Incentive is 60 Per cent while State share is 40 Per cent.
Rural Infrastructure:
Rural Non-Farm Development Agency (RUDA)
Rural Non-Farm Development Agency (RUDA) was established in November 1995 by the Government of Rajasthan as an independent agency to promote the Rural Non-Farm Sector (RNFS) in the state. RUDA carries out its activities in 3 major sub sectors:
• Leather
• Wool & Textile
• Minor Mineral (SCP)
In addition to the above, sector market support and coordination is another major activity of RUDA. State Plan head is the main source of funding for RUDA activities.
Geographical Indication (GI) Registration
• RUDA has obtained GI Registration for crafts like, Pokran Pottery, Blue Pottery, Kota Doria and Sanganer & Bagru handblock print under its Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) initiatives.
Rural Roads:
• It has been shown that a paved surface in reasonable good condition can contribute 15 to 40 per cent saving in vehicle operation cost. Village road length in the state is 1,75,937.49 Kms (as of 31.03.2019).
• As per budget announcement of 2019-20 Wall to Wall Vikas Path in each Gram Panchayat would be constructed in next five years. Vikas Path is to be constructed by cement concrete block with covered drains and utility services etc. Selection of village and alignment of Vikas Path will be done by a District Level Committee.
Van Dhan Yojana
• The state government has decided to implement Van Dhan Yojana in Modified Area Development Agency (MADA) areas in Rajasthan along with tribal sub-plan and Sahariya localities.
• For this, a district-level coordination and monitoring committee has been formed under the chairmanship of the district collector. Additionally, the project officer (MADA) will be the district nodal officer (MADA area) for implementation of Van Dhan Yojana and additional commissioner (first) tribal area development department, Udaipur, will be the state nodal officer (MADA area).
Electricity
• Deen Dayal Upadhyay Gramin Joyti Yojana (DDUGJY) – The DDUGJY is implemented in the State to strengthen rural electricity distribution network and to electrify RHHs of Abadi areas.
• Saubhagya Yojna – Prime Minister has launched Pradhan Mantri Sahaj Bijli Har GharYojana – “Saubhagya” on 25 September, 2017 to provide electricity to all willing households in the country in rural as well as urban areas. Government of Rajasthan is also participating in the Saubhagya to provide electricity to expect left outs after implementation of DDUGJY scheme.
• Integrated Power Distribution System (IPDS) – Under IPDS 185 towns has been covered in Rajasthan for system strengthening and reduction in Aggregate Technical & Commercial (AT&C) loss in urban areas.
• Ujwal Discom Assurance Yojana (UDAY) – Ujwal Discom Assurance Yojana for financially turnaround of Power Distribution Companies has been launched by the Government of India with an objective to improve the operational and financial efficiency of the State Discoms.
• Unnat Jyoti by Affordable LEDs for All (UJALA) – In an effort to spread the message of utilizing energy efficient equipments, Government of Rajasthan with the help of Energy Efficiency Service Limited, (Government of India undertaking) promoted the use of energy efficient appliances – LED bulbs, Tube Lights and Fans. Under the scheme 1,02,182 Energy Efficient Fans, 163.92 Lakh LEDs and 3.10 Lakh Tube lights (20 Watt) have been distributed.
Renewable Energy
• Rajasthan Renewable Energy Corporation Ltd. (RRECL) is the State Nodal Agency of Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) for generation of energy from non-conventional energy sources in the state and is also the State Designated Agency for promoting energy efficiency and energy conservation.
Solar Energy – KUSUM Scheme
• The Union Budget 2018 announced Kisan Urja Suraksha evam Uhaan Mahaabhiyan (KUSUM) to replace diesel pumps and grid-connected electric tube-wells for irrigation by solar irrigation pumps (SIPs) with a buy-back arrangement for farmer’s surplus solar energy at a remunerative prices.
Objectives of Kusum Scheme:
• Water security to farmers through reliable Solar power.
• Utilization of degraded land of farmers.
• Additional income to farmers by selling surplus power to DISCOM.
• Water conservation.
• Promotion of decentralized Solar power generation.
• Reduction of burden of subsidy to agriculture sector.
Service Sector
Religious Tourism
• Devasthan department is engaged in protection and promotion of religious culture. 390 state direct charge and 203 state self-sufficient temples and institutions are managed directly by the department.
Schemes:
• Senior Citizen Tirtha Yatra Yojana
• Kailash Mansarovar Tirtha Yatra Yojana
Information Technology & Communication
Jan Soochna Portal:
In order to provide information of government services to the citizens in an accessible, transparent and reliable manner, the portals related to various projects are currently being developed, based on the suggestions received from the concerned department.
1. In this endeavor, the Jan Soochna Portal was inaugurated on 13 September, 2019.
2. Jan Soochna Portal has been created by the department to provide information about all the schemes implemented by the government in one place, which will be updated from time to time.
3. Jan Soochna Portal has been made available information of 49 schemes running in 25 departments.
Rajasthan Startup:
• As part of State Government’s mandate to give a thrust to the state’s Startup sector, several initiatives have been implemented.
• The iStart Portal (istart.rajasthan.gov.in) works as a single window for Startups.
• In addition, Challenge for Change, Rajasthan Stack, QRate ranking mechanism and an incubator, iStart Nest (Jaipur, Kota and Udaipur), are also made available to the State’s Startups.
Rajasthan Sampark Portal:
• Rajasthan Sampark Portal is being used as centralized grievance redressal platform.
• Add-on modules like – mobile app, reality check module, GIS integration and applications like advance data analytics have been developed and implemented for enhanced user experience.
• Reality check module with Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) functionality has been integrated with Rajasthan Sampark Portal.
• A new toll free number (181) for the CM Helpline has been activated.
E-Mitra:
• Presently more than 500 services of government departments / private organisations are being provided electronically through more than 70,000 e-mitra Kiosks to the citizens of the State.
• Simultaneously, deposition of utility bills through mobile application has also been started.
E-MitraPlus:
• eMitraPlus is a revolutionary step ahead in eService delivery. It provides the services directly, without any human interface, just as an ATM does.
• eMitraPlus is the first of its in India.
• One can apply for government documents like birth certificate, domicile certificate etc. and get print through in-built printer.
• It allows multiple payment modes such as cash, debit / credit card, net banking.
• eMitraPlus is enabled with Video conferencing facility to residents for registering their feedback and problems directly to the officials. These Kiosks are available at rural and urban areas of the state.
• More than 13,961 eMitraPlus Kiosks has been installed.
Urban Development
Chief Minister Teachers’ Housing Scheme and Chief Minister Prahari Awas Yojana:
• provide houses to state awarded teachers, the board is ready to give houses in its schemes as per city wise / category wise availability of houses on the discounted prices once the society of awarded teachers is being constituted.
• On 20 December, 2019 RHB has launched two housing schemes for teachers & praharis (Constables) under the flagship name of “Chief Minister Teachers Housing Scheme” and “Chief Minister Prahari Awas Yojana”.
Deendayal Antyodaya Yojna
• National Urban Livelihood Mission Swaran Jayanti Shahri Rozgar Yojana (SJSRY) has been rerstructured as Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana- national urban Tivelihood Mission DAY-NUTM). The mission is being implemented in 193 urban Tocal Bodies of Rajasthan.
Components of the NUTM are as under:
• Capacity Building and Training (CB&T)
• Social Mobilization and Institution Development (SM & ID)
• Employment through Skill Training and Placement (EST&P)
• Self-Employment Programme (SEP)
• Support to urban Street vendors (SuSv)
• Scheme of Shelter for urban Homeless (Sufi)
• Innovative and Special Projects
Shahari Jan Sahbhagi Yojana (SJSY)
• The scheme was started by the State Government in December, 2004 to ensure public partnership in urban development.
• The two main components of the scheme are general public awareness and development works. General public awareness is generated through organizing camps, seminars and workshops (regarding sanitation, public heath, water storage, roads, construction of school /hospital and office buildings) to see public participation.
Urban Infrastructure Development Scheme for Small and Medium Towns (UIDSSMT)
• The Central Government has launched this scheme with the objective of providing basic infrastructure services to the urban poor in the small and medium size towns. This scheme is applicable to all cities/towns except cities/towns selected under Jawaharlal Nehru National Urban Renewal Mission (JNNURM).
• Ministry of urban development (MOUD) has changed the funding pattern to 60:20:20 (Gol:State:UEB) as per AMRUT funding pattern for 11 projects in progress. The Rajasthan Urban Drinking Water, Sewerage and Infrastructure Corporation Etd. (RUDSICO) has been nominated as the nodal agency for implementing this scheme in the State.
Rajiv Awas Yojana (RAY)
• Slum Free City Plan of Action (SFCPoA) of Ajmer city under RAY Scheme has been approved by Government of India.
• Draft SFCPoA of Jaipur, Jodhpur, Kota, Bharatpur, Bikaner, Alwar, Pratapgarh and Chittorgarh have also been prepared.
• All RAY projects have been subsumed under “blousing for All” by Gol.
Rajasthan Urban Development Fund (RUDF)
• Government of Rajasthan has established Rajasthan urban Development Fund (RuDF) on 26.03.2010.
• The Rajasthan urban Development fund (RuDF) is a fund created by the Government of Rajasthan to ensure comprehensive development of the urban areas across the State. Rajasthan urban Drinking Water Sewerage and Infrastructure Corporation Ltd (RuDSICO) is working as nodel agency for RuDF.
Smart Cities Mission:
• Smart City Mission was launched by Gol in June, 2015 to promote cities that provide core infrastructure and give a decent quality of life to their citizens, a clean and sustainable environment and application of Smart Solutions.
• The mission will cover 100 cities & its duration will be five years. 100 crore per city for 5 years are to be given as grant by government of India and an equal amount will be contributed by State/ ULB. A total of 4 cities were shortlisted in Rajasthan to be developed as Smart Cities, namely Jaipur, udaipur, Kota & Ajmer.
AMRUT Mission:
• Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and urban Transformation (AMRuT) was launched by Hon ble Prime Minister of India in June, 2015. 29 cities in Rajasthan are selected under AMRuT i.e. Alwar, Beawar, Si ar, nagaur, Bhiwadi, Pali, SawaiMadhopur, Tonk , Hanumangarh, Bundi, Sujangarh, Dholpur, Gangapur City, Chittorgarh, Bhilwara, Sri Ganganagar, Churu, Jhunjhunu, Baran, Kishangarh, Hindaun City, Jaipur, Jodhpur, Ajmer,Kota, Bikaner, Udaipur, Bharatpur and Jhalawar.
• The sectors identified under this mission are Water Supply, Sewerage & Septage, Drainage, urban Transport and Green Spaces.
LED Light Project
• Energy saving Project has been initiated in the State to save energy in Street Light Sector.
• The aim of the project is to increase the illumination level on roads and to reduce the electricity consumption.
Swachh Bharat Mission (Urban)
• It is aimed to achieve better level of cleanliness all over India through public participation and active public support upto 31st March 2020.
• Under Swachh Bharat Mission activities, such as construction of personal deomestic toilets, community/ public toilets, and activities of urban solid waste management in concerned urban areas are to be implemented. Under USBM, Quality Council of India has certified all ULB’s at-least once.
Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (Urban):
• This housing scheme aims to provide affordable house to the homeless Economically Weaker Section with annual income up to 3.00 lakh and Lower Income Group with Annual income 3.00 to 6.00 lakh.
