Industrial Sector of Rajasthan
Background
Industrialisation is considered one of the foremost modus to stimulate the overall growth of the country.
Additionally, development of industries has the vast potential of providing substantial employment and generating the income and improving the standard of living and over all well-being of the people.
At the time of Independence, the state had inherited poor status in respect of development of industries.
Until 1960, Rajasthan virtually had no place on the industrial map of India. Some strategies were worked out to increase investment in public sector industries and to promote private sector investment in different districts, which gradually led to the development of industries in the state.
In terms of production value, the textile industry, dominates the large and medium category of industries.
This is followed by industries catering to agro-based, food and allied products; cement and cement products: chemical gases, lubricants and plastic; heavy machinery; metal allied products, automobile parts and machine tools parts; electrical and electronics -related products; minerals , stones and lime; drugs and pharmaceuticals; ceramics and glass wares; and leather and footwear.
The state is almost the sole producer in the country of certain minerals like wollastonite, zinc and copper.
Besides this, it is also a leading producer of crops such as mustard, bajra, barley, maize, cotton and spices.
There is also a huge population of livestock that sustains the livelihoods of several communities across the state.
Contribution of Industries to State GDP
The sectoral contribution of the Industries sector in the total Gross State Value Added (GSVA) of the state stands at 27.81 per cent at current prices in 2019-20.
The contribution of manufacturing and mining sector to GSVA at current prices is 9.82 per cent and 6.62 per cent respectively in 2019-20.
Contribution within Industrial Sector:
• Manufacturing – 35.28 %
• Construction -11.73 %
• Mining -23.79 %
• Electricity, Gas & other Utility Services – 29.18%
Contribution of Industries in Employment
In 1960-61, total employment in industries and mines was estimated at 6.2 lakh (i.e., 8 per cent of the total number of workers) and this increased to 10.26 lakh by 1998-99, a rise of 64 per cent.
Currently, the services sector employed 47% of the state’s population, followed by the agriculture (44%) and Industrial (8%) sector.
Hence, though growth in Industrial sector may appear impressive, industry’s percentage share in total employment is not significant.
Industrial Profile of Rajasthan
A. On Basis Size of Factory/Investment in Plant & Machinery
Large Scale Industries in Rajasthan
• Number: 390
• Employment: 2,00,764
Medium Scale Industries in Rajasthan
• Number: 254
• Employment: 25,597
Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises
• Numbers: 8,78,689
• Employment: 40,81,394
Definitions:
In accordance with the provision of Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises Development (MSMED) Act, 2006 the Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME) are classified in two Classes:
• The Manufacturing Enterprises are defined in terms of investment in Plant & Machinery.
• The enterprises engaged in providing or rendering of services and are defined in terms of investment in equipment.

B. On Basis of Products:
• Basic Goods Industries:
o Cement, basic chemicals, Steel, fertilisers, electricity, copper, zinc etc.
• Capital Goods Industries
o Industries that produce machinery required for industries, transport equipment etc.
o Hindustan Machine Tools (Ajmer), Instrumentation Ltd (Kota).
• Intermediate Goods Industries
o Industries that produce goods used as raw materials by other industries
o Tyres (JK Tyre, Kankroli), Cotton yarn
• Consumer Goods Industries
o Durable goods: Scooters, Automotive units
o Non-durable: Edible Oils, Agro-based
C. On basis of Raw Material used:
• Agro-based Industries
• Forest-based Industries
• Mineral based Industries
• Livestock based Industries
Rural Industries: Cottage & Handicrafts of Rajasthan
Handloom and handicrafts constitute the largest part of Indian cottage industries.
Handicrafts help preserve traditional art and culture, while the handloom sub-sector is an important source of employment generation.
Handlooms, handicrafts, khadi and village industries constitute an important part of the non-formal sector of Rajasthan’s economy.

Exports:
The state government has identified exports as one of the thrust areas for economic development.
The significance of exports from the state lies not only in earning foreign exchange for the country’s exchequer but also in indirect benefits to the state such as: expansion of market opportunities for its produce, improvement in product quality and subsequent handling techniques, technological up gradation in terms of plant, machinery and manufacturing process, greater employment opportunities etc.
Rajasthan has been growing strong in exports.
The total exports in financial year 2018-19 stands at 51,178.41 crore which registered a growth of 10.11 per cent over the previous year 2017-18.
The top five export items from Rajasthan accounts for more than 50 per cent of exports from the State. These include:
• Engineering goods
• Textiles
• Chemical and allied products
• Gems and jewellery
• Handicrafts
Export Promotion Initiatives:
State Level Exports Award Scheme:
The scheme was declared in the Industrial Policy, 1994 with the objective of encouraging exporters of the State.
There is provision for selection of 31 outstanding exporters in 16 categories.
Under this, one best exporter per year in the State will also be awarded with “Lifetime Achievement Export Ratna Award”.
Export Promotion Council
• To encourage export in the State “Rajasthan Export Promotion Council” and “Rajasthan Export Promotion Coordination Council” were formed.
Key Industries in Rajasthan
Rajasthan is home to several key industries which are engaged in production of goods like cotton cloth, cotton yarn, cement, sugar, urea, zinc-ingots, ball-bearings, edible oils, salt, copper cathodes etc.
All of these Industries, do not belong only to large scale Units but may also belong to Small or medium scale units but they play a key role in economy of Rajasthan in terms of Revenue, employment etc.
Cement
• Rajasthan has 24 major cement plants, having a total capacity of 55 million tonnes per annum (MTPA). It is the largest cement-producing state in India.
• The state has about 17% share in cement grade limestone reserves of India. Gypsum is also available in the state but coal is imported from outside the state.
Mining & Minerals
• Rajasthan has deposits of 81 different types of major and minor minerals. Out of these, 57 minerals are being currently mined.
• Rajasthan is the sole producer of:
o Lead & Zinc ores
o Selenite
o Wollastonite
• Rajasthan is leading producer of:
o Silver
o Calcite
o Gypsum
o Ball Clay
o Feldspar
o Rock Phospate
o Steatite
o Red Ochre
o Steel & Cement grade limestone
• It also has prominent position in the country in the production of dimensional and decorative stones, such as marble, sandstone, granite etc.
• 70% of Bone-China tableware is produced in Rajasthan.
• There are 187 mining leases for major minerals, 14,420 mining leases for minor mineral and 17,534 quarry licenses in the state.
• Rajasthan as a state accounts for 90% of India’s marble, slate and sandstone production and has a monopoly in other ceramic minerals.
Auto and Auto Components
• Alwar and Jaipur districts are close to major auto production hubs of the country such as Noida (Uttar Pradesh), Gurgaon and Dharuhera (Haryana); offering excellent advantages for setting up of auto and auto ancillary units.
• Over 100 units are currently functional in Bhiwadi, Neemrana and Pathredi in Alwar district, Rajasthan. These are the 3 main auto clusters in Rajasthan.
• Neemrana-Japanese zone: A 1,167-acre industrial area in Neemrana has been developed especially for industrial units from Japan. Automotive units of Nissin Brakes, TPR Auto parts, Takata India, Nippon Steel, Toyota Gosei, Mikuni India and Toyota Kirloskar Motor are present in this zone.
Textile
• Rajasthan has a leading position in the production of polyester viscose yarn and synthetic suiting material as well as processing of low-cost, low-weight fabric (at Pali, Balotra, Sanganer and Bagru).
• Bhilwara has emerged as India’s largest manufacturer of suiting fabrics and yarn.
• Jaipur is a well-known centre for manufacturing garments, primarily for exports.
IT and ITeS
• Rajasthan is emerging as one of the best locations in India to invest in the IT / ITeS sector.
• IT parks with special infrastructure have been set up at Jaipur, Jodhpur, Udaipur, Kota and Alwar.
Agro-based industry
• Rajasthan is the largest producer of rapeseed, bajra, guar seed, spices such as fenugreek, coriander, cumin, fennel and mustard.
• It is the second largest producer of oilseeds and spices and the third largest producer of soya bean and coarse cereals in India.
Chemicals
• The key chemicals produced in Rajasthan include fertilisers, caustic soda and pesticides.
• The principal industrial complexes for chemicals are at Jaipur, Kota, Udaipur and Bhilwara.
Gems and jewellery
• Rajasthan is a store house of many precious and semi-precious stones such as emeralds, aquamarines, heliodors, corundums, diamonds, epidotes, topazes, tourmalines, amethysts, crystal quartzes, garnets, and green and blue quartzites.
• Rajasthan is the largest production centre of coloured precious and semi-precious stones as well as the largest manufacturer of cut and polished diamonds in the country.
• The state has a wide pool of skilled manpower along with several training institutions.
Steel
• Rajasthan’s steel industry comprises re-rolling and stainless steel units located mainly in Jodhpur, Alwar and Jaipur.
• Most of the re-rolling units belong to the small scale sector.
Ceramics
• Rajasthan has abundant slip clay, pottery clay, retort clay, terracotta clay, pipe clay, bleaching clay, bonding clay etc., which are used for manufacturing bricks, tiles, statues, insulators, porcelain (via a mixture clay with felspar and quartz) etc.
• Glass and ceramic units are among the thrust sectors identified in the 1988 Industrial Policy.
• Units are concentrated in Jaipur, Bikaner, Bhilwara, Abu Road and and Bhiwandi.
• Rajasthan is a major producer of felspar, quartz and bentonite, which are the raw materials for Ceramic Industry.
Salt
• Rajasthan is the third largest producer of salt (sodium chloride) in the country and accounts for the country’s one-tenth of salt production.
Energy
• Highest solar energy potential in India – 142 GW
• Rajasthan shines on the solar map of India with 300-330 clear sunny days, comparable to deserts of California and Nevada.
• Within the state, the districts such as Barmer, Bikaner, Jaisalmer and Jodhpur are the key regions with the best solar radiation.
• Rajasthan is endowed with two critical resources that are essential to solar power production: high level of solar radiation (6-7 kWh / m2 / day) and large tracts of relatively flat, undeveloped land.
• Rajasthan has wind energy potential of 18.7 GW
Oil and Gas
Rajasthan is a significant producer of crude oil in India.
The State contributes about 22-23 per cent (7.5 Million Metric Tonnes Per Annum) to total crude oil production (34 MMTPA) in India and is the second largest producer after Bombay High which contributes about 40 per cent.
Petroleum producing area in the state is spread over an area of about 1,50,000 sq. km (14 districts) under 4 Petroliferous Basins.
• Barmer-Sanchor Basin – (Barmer, Jalore districts)
• Jaisalmer Basin – (Jaisalmer district)
• Bikaner-Nagaur Basin – (Bikaner, Nagaur, SriGanganagar, Hanumangarh, Churu districts)
• Vindhyan Basin – (Kota, Baran, Bundi, Jhalawar, part of Bhilwara & Chittorgarh districts)
The Directorate of Petroleum was setup to expedite the exploration and development programme of Oil and Natural Gas in the State.
HPCL Rajasthan Refinery Limited, Pachpadra, Barmer
Prime Minister on 16.01.2018 has commenced work for 9 MMTPA Rajasthan Refinery at Pachpadra, Barmer.
Highlights of the Project are as follows:
• First of its kind in India i.e. integrated with Petrochemical complex.
• Project cost – Rs. 43,129 crore
• This Project is a Joint Venture in which HPCL’s share is 74 percent and Government of Rajasthan’s share is 26 percent.
Departments & Organisations
Rajasthan is a third-most leading investment destination in India after Maharashtra and Gujarat on account of better law and order situation, peaceful environment, excellent transport & power infrastructure, investment friendly climate and very less population density.
Various departments/corporations /agencies are functional in the state to promote industrial development and for facilitating establishment and expansion of small, medium and large scale industries and meeting their various requirements, either directly or by discharging the responsibility as the strong facilitators.
Key Departments & Organisation is Rajasthan for development of Industries:
Industries Department, GoR
Commissionerate of Industries is the nodal department with prime motive to promote the development of industries and handicrafts in the State.
The department operates through 36 District Industries Centres (DICs) working in the State. Additionally, 7 District Industries Sub-Centres have also been established at Abu Road, Balotra, Beawar, Faina, Kishangarh, Makrana and Neemrana.
These centres have been set up to cater to the needs of small scale industries of the area. The Industries Department is located at Udyog Bhawan, Tilak Marg, Jaipur.
Bureau of Investment Promotion (BIP)
Bureau of Investment Promotion (BIP), established in 1991, is the nodal agency for investment promotion in the state.
BIP serves as a one-stop knowledge house with respect throughout the ‘conceptualisation-to-commissioning’ stage.
The most important role of BIP is in facilitating speedy clearances from various departments, addressing investment concerns and clearing bottlenecks.
BIP is the nodal agency for investments of more than Rs. 10 crore under the Single Window System.
As a core responsibility to promote Rajasthan as an investment destination, BIP participates & organises key conferences throughout the year including the Resurgent Rajasthan Summit.
Rajasthan State Industrial Development and Investment Corporation (RIICO)
RIICO is an apex organisation engaged in fostering the growth of industrialization in the State.
The mission of RIICO is to catalyze planned and rapid industrialization of Rajasthan.
RIICO has set up 28 Regional Offices all over Rajasthan to administer the development and management of the industrial areas.
RIICO has pioneered industrialisation of the state of Rajasthan by setting up of industrial areas.
RIICO also acts as a financial institution by providing loan to large, medium and small scale projects.
Role of RIICO:
• Identifying investment opportunities.
• Providing access to information that is critical for setting up of projects.
• Assisting translation of investment possibilities into concrete investment proposals.
• Nodal agency for single-window clearances.
• Facilitation on behalf of investors with all Government departments / agencies to ensure that proposals get immediate attention.
• Assisting in site selection and obtaining infrastructural facilities.
• Interfacing with Government departments for required clearances.
Rajasthan Export Promotion Council
Rajasthan Export Promotion Council has been setup to develop, promote and support export-oriented industries along with allied activities in Rajasthan.
The Chief Minister has approved for setting-up of the Rajasthan Export Promotion Council under the Companies Act, 2013.
Major Responsibilities:
Major responsibility of the Rajasthan Export Promotion Council are to provide technical guidance and sharing of information and expert advice in regard to the demand of exports for various products, formalities required to be completed, coordination, counselling or financial support along with arrangements of conventions, business meetings and seminars, publication and distribution of promotional literature and providing international or national platforms to the exporters and other businessmen for promotion of their trades.
The Council will also issue documents like ‘Certificate of Origin’ or ‘Registration-cum-Membership Certificate’ to the exporters.
Rajasthan Export Promotion Coordination Council (REPCC)
Rajasthan Export Promotion Coordination Council (REPCC) has been setup to provide guidance to the exporters and coordinate between different industrial organizations, exporters or various state government departments to remove difficulties in export of various goods and services.
Major Functions of REPCC:
The Council will support in developing basic infrastructural facilities required for expansion of export from Rajasthan and coordinate with various departments and enterprises of the Government of India for promotion of exports.
It will also play important role in organizing international, national or state- level fairs & exhibitions, workshops, conventions, business meets or seminars etc. for expansion of export business.
The Coordination Council will constitute sector-wise committees or special panels for development of businesses in handicraft, textiles, agriculture, gems-jewellery sectors or region-wise committees for Mewar, Marwar, Hadauti and Shekhawati regions.
Rajasthan Small Industries Corporation Limited (RAJSICO)
The Rajasthan Small Industries Corporation Limited was established in June, 1961 mainly to provide assistance to small scale industries and artisans, to facilitate marketing of their products.
The Corporation purchases selected handicraft items directly from the craft persons through its central stores and markets them through its outlets RAJASTHALI situated at Jaipur, Udaipur, Mount Abu, Amber, Agra, Delhi, Kolkata, Mumbai.
Rajasthan Financial Corporation (RFC)
Rajasthan Financial Corporation (RFC) was established in the year 1955 under the State Financial Corporations Act, 1951 with the basic object of fostering financial needs for setting up of new industries, expansion and renovation of existing one, upto Rs. 20 crore.
RFC provides medium- and long-term loans for new industrial units in the SME sector.
PDCOR Limited
PDCOR Limited (PDCOR) is a company jointly promoted by the Government of Rajasthan and Infrastructure Leasing & Financial Services Limited (IL&FS) to facilitate private sector investment in the infrastructure sector of Rajasthan.
Rural Non-Farm Development Agency (RUDA)
Rural Non-Farm Development Agency (RUDA) was established in November, 1995 by the Government of Rajasthan as an independent agency to promote the Rural Non-Farm Sector (RNFS) in the state.
RUDA carries out its activities in 3 major sub sectors which are as follows:
• Leather
• Wool & Textile
• Minor Minerals
RUDA has obtained GI Registration for craft like Blue Pottery, Kota Doria and Sanganer & Bagru Handblock print under its Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) initiatives.
Additionally, sector market support and co-ordination is another major activity of RUDA.
Rajasthan Khadi & Village Industries Board
Khadi & Village Industries Board was established to provide employment to artisans of unorganized sector, to provide help in production of high quality products, to provide training to artisans, and to inculcate the feeling of self-reliance.
Rajasthan Khadi & Village Industries Board has played important role in providing self-employment in rural areas of Rajasthan.
Rajasthan State Handloom Development Corporation (RHDC)
Rajasthan State Handloom Development Corporation was constituted in 1984 with the main objective to promote the cotton handloom textile sector of Rajasthan.
It plays a pivotal role in skill upgradation, design & development and market facilitation or traditional weavers and artisans of the state in modern techniques.
Index of Industrial Production (IIP)
The Index of Industrial Production (IIP) is an index in India which details out the growth of various sectors in an economy.
It is a short-term micro economic indicator widely used in measuring the industrial growth of the State by comparing the general level of industrial activities in the economy in current year with reference to a base year.
The index indicates the relative change over time in the volume of production in industrial sector and is an effective tool to measure the trend of current industrial production.
How is IIP in Rajasthan calculated?
The Index of Industrial Production (IIP) compares the growth in the general level of industrial activities in the economy with reference to a comparable base year.
• The Directorate of Economics and Statistics, Department of Planning, Rajasthan has been compiling / releasing index of industrial production for Rajasthan since 1971 as per the guidelines of the Central Statistical Office (CSO), Govt. of India.
• The IIP is the leading Indicator for industrial performance in the State, compiled on a monthly basis.
• The IIP series (Base 2011-12) is based on 154 items / product groups aggregated into three broad groups of:
o Manufacturing
o Mining
o Electricity
• A web portal has been developed for IIP and online data entry is being done, through District Statistical Offices.
IIP Index for Rajasthan

Public Sector Enterprises
Public Sector Enterprises play an important role in the planned development of the state. They are formulated to speedup growth of infrastructure, increase employment opportunities, secure public welfare and help reduce regional imbalances in development.
Public Sector Enterprises functioning in Rajasthan fall into two categories:
• Public Enterprises setup by Union (Central) Government
• Public Enterprises setup by State Government
Types of Public Sector Enterprises:
There are three different forms of organisation used for the public sector enterprises in India. These are:
• Departmental Undertaking
• Statutory (or Public) Corporation
• Government Company
Departmental Undertaking: form of organisation is primarily used for provision of essential services such as railways, postal services, broadcasting etc.
Such organisations function under the overall control of a ministry of the Government and are financed and controlled in the same way as any other government department.
This form is considered suitable for activities where the government desires to have control over them in view of the public interest.
Statutory Corporation (or public corporation) refers to a corporate body created by the Parliament or State Legislature by a special Act which define its powers, functions and pattern of management.
Statutory corporation is also known as public corporation. Its capital is wholly provided by the government.
Examples of such organisations are Life Insurance Corporation of India, State Trading Corporation etc.
Government Company refers to the company in which 51 percent or more of the paid up capital is held by the government.
It is registered under the Companies Act and is fully governed by the provisions of the Act.
Most business units owned and managed by government fall in this category.
Public Sector Enterprises by Union Government functioning in Rajasthan:
• FCI Aravali Gypsum & Minerals Limited, Jodhpur
• Hindustan Salts Ltd, Jaipur
• HPCL Rajasthan Refinery Ltd., Pachpadra, Barmer
• Instrumentation Ltd., Kota
• Rajasthan Drugs and Pharmaceuticals Ltd., Jaipur
• Rajasthan Electronics and Instruments Ltd (REIL), Jaipur
• Sambhar Salts Ltd., Jaipur
Public Sector Enterprises by State Government:
The State Public Sector Undertakings (PSUs) consist of State Government Companies and Statutory Corporations.
The State PSUs are established to carry out activities of commercial nature keeping in view the welfare of people and occupy an important place in the State economy.
There are 43 PSUs including 40 Government Companies & 3 Statutory Corporations.
The State PSU’s employee close to 1 lakh people, have an annual turnover of about 8.27% of SGDP (2018) and earned a profit of about 1,822 Crores annually.
Role of State Government and Legislature:
The State Government exercises control over the affairs of these PSUs through its administrative departments.
State Government appoints the Chief Executive and Directors to the Board.
The State Legislature also monitors the accounting and utilisation of Government investment in the PSUs.
The CAG reports are placed before State Legislature.
Bureau of Public Sector Enterprises (BPE)
Bureau of Public Enterprises (BPE) was constituted under the administrative control of State Enterprises Department.
BPE obtains quarterly performance reports and annual reports from the PSUs and evaluates them.
Based on the evaluations necessary directions are given to the PSUs for improvement in their performance.
Important State Public Sector Enterprises: Statutory Corporations/ Boards
• Rajasthan State Road Transport Corporation
• Rajasthan Financial Corporation
• Rajasthan Land Development Corporation
• Rajasthan Housing Board
• Rajasthan State Warehousing Corporation
• Rajasthan State Agriculture Marketing Board
Important State Public Sector Enterprises: Registered Companies
Infrastructure Related State Public Sector Enterprises
• Power
o Rajasthan Rajya Vidyut Utpadan Nigam Ltd,
o Rajasthan Rajya Vidyut Prasaran Nigam Ltd,
o Jaipur Vidyut Vitran Nigam Ltd.
o Ajmer Vidyut Vitran Nigam Ltd,
o Jodhpur Vidyut Vitran Nigam Ltd.
• Renewable Energy
o Rajasthan Renewal Energy Corporation Ltd.
• Roads
o Rajasthan State Road Development & Construction Corporation Ltd.
• Water:
o Rajasthan Jal Vikas Nigam Ltd.
Industry Related State Public Sector Enterprises
• Rajasthan State Industrial Development & Investment Corporation Ltd. (RICCO)
• Rajasthan State Mines & Minerals Ltd.
• The Rajasthan Small Industries Corporation Ltd.
• Rajasthan State Handloom Development Corporation Ltd.
• Rajasthan State Ganganagar Sugar Mills Ltd.
Tourism Related State Public Sector Enterprises:
• Rajasthan Rajya Paryatan Vikas Nigam Ltd.
• Rajasthan State Hotels Corporation Ltd.
Agriculture Related State Public Sector Enterprises:
• Rajasthan State Seeds Corporation Ltd.
• Rajasthan State Agro Industries Corporation Ltd.
Geographical Indications
A geographical indication (GI) is a name or sign used on certain products which corresponds to a specific geographical location or origin (e.g. a town, region, or country).
GIs have been defined in GIs have been defined under Article 22(1) of the WTO Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) Agreement.
A GI is registered for an initial period of ten years, which may be renewed from time to time.
India being member of WTO enacted the Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act, 1999 or protection of geographical indications in India.
Darjeeling Tea was the first Indian product to get the geographical indication tag.
What is the Significance of GI Tag?
Like other intellectual properties rights (example: Copyright, Patent, Trademark etc.), Geographical Indication tag also provides similar rights and protection to holders.
The GI tag ensures that none other than those registered as authorised users (or at least those residing inside the geographic territory) are allowed to use the popular product name.
Geographical Indications in Rajasthan
S.No. GI Famous Places in Rajasthan
1 Pokaran Pottery Pokaran
2 Phulkari Kota
3 Blue Pottery Jaipur
4 Molela Clay Work Molela, Nathdwara (Rajsamand)
5 Kathputlis of Rajasthan Rajasthan
6 Sanganeri Hand Block Printing Jaipur
7 Bikaneri Bhujia Bikaner
8 Kota Doria Kota
9 Bagru Hand Block Print Jaipur
10 Thewa Art Work Pratapgarh
11 Makrana marble Makrana, Nagaur
DMIC
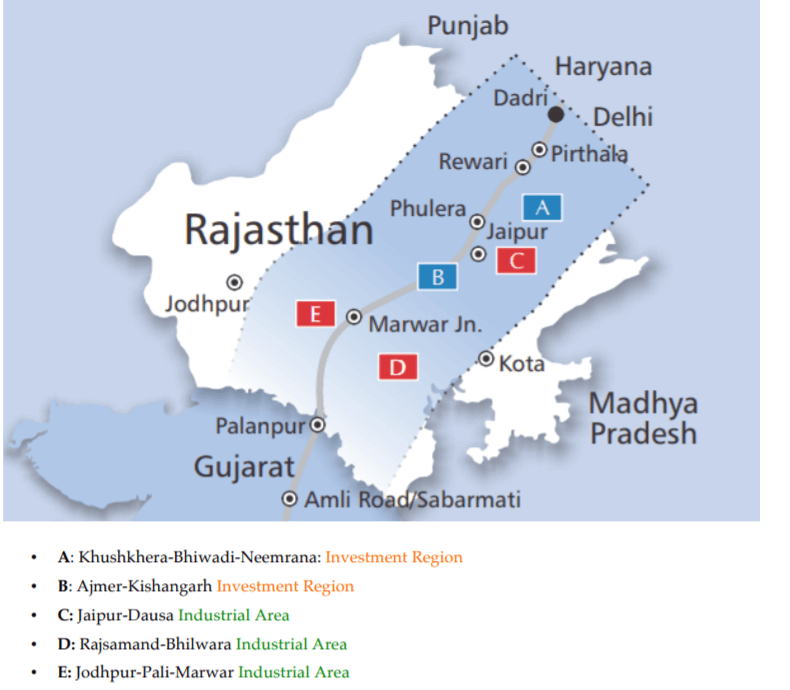
Delhi – Mumbai Industrial Corridor (DMIC) is India’s most ambitious infrastructure programme aiming to develop new industrial cities as ‘Smart Cities‘ and converging next generation technologies across infrastructure sectors.
It is a mega infra-structure project of USD 100 billion, covering an overall length of 1483 kms between Delhi and Mumbai.
DMIC is being developed as a “Global Manufacturing and Trading Hub”, providing a major impetus to planned urbanization in India with manufacturing as the key driver.
In addition to new Industrial Cities, the programme envisages development of infrastructure linkages like power plants, assured water supply, high capacity transportation and logistics facilities as well as softer interventions like skill development programme for employment of the local populace.
It incorporates 9 Mega Industrial zones, high-speed freight line, 3 ports, and 6 airports; a 6-lane intersection-free expressway connecting Mumbai & Delhi and a 4000 MW power plant.
A Dedicated Freight Corridor (DFC) between Dadri (UP) and Jawahar Lal Nehru Port (Mumbai) is being constructed which covers a total length of 1,483 km.
About 39 per cent of the Corridor passes through Rajasthan.
A band of 150 km (Influence region) has been chosen on both the sides of the Freight corridor to be developed as Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor (DMIC).
DMIC spans the states of
• Uttar Pradesh
• Haryana
• Rajasthan
• Madhya Pradesh
• Gujarat
• Maharashtra
DMICDC
DMIC Development Corporation (DMICDC) incorporated in 2008, is the implementing agency for the project.
DMICDC has been registered as a company with 49% equity of Government of India, 26% equity of the JBIC (Japan Bank for International Cooperation) and the remaining held by government financial institutions.
Components of DMIC
• Eight manufacturing cities (2 in Rajasthan) will be developed in Phase – I:
o Khushkheda-Bhiwadi-Neemrana Investment Region having an area of about 165sq. kms and encompassing 42 villages of Alwar district
o Jodhpur-Pali-Marwar Industrial Area (JPMIA) being developed in the area close to 154 sq. kms, encompassing 9 villages of Pali district.
• High Speed – High Capacity connectivity backbone provided by Western Dedicated Freight Corridor (DFC).
• 24 manufacturing cities (Investment Region, IR and Investment Area, IA) are envisioned in the master plan.
• 2 Airports – Aerotropolis, Bhiwadi, Alwar, Rajasthan & Greenfield International Airport, Dholera, Gujarat.
Why DMIC is Important for Rajasthan:
• Over 58% area of the Rajasthan falls within the influence area of DMIC
• 39% of Dedicated Freight Corridor (DFC)
• Rajasthan has rich agricultural and mineral base for industries like Cement, Building Stones, Gypsum, Gems & Jewellery, Chemical, Food processing, Textiles
• Emerging sectors include IT / ITES, Auto Component and Knowledge Hubs.
DMIC in Rajasthan:
Based on the strengths of specific regions across the state, five development nodes are identified in the influence area of DMIC.
It includes two investment regions and three industrial areas. Proposed project components in each of the nodes are