CURRENT AFFAIRS
JANUARY 2021
JUDICIAL ACTIVISM AND JUDICIAL OVERREACH
The act of the Supreme Court staying implementation of three farm laws was seen by many as an act of judicial activism/overreach.
Judicial activism and Judicial overreach
• Judicial activism: Judicial activism is a judicial philosophy that motivates judges to depart from the traditional precedents in favour of progressive and new social policies. Judicial activism is manifested when the Supreme Court (or High Court) becomes an activist and compels the authority to act and sometimes also direct the government, government policies and also administration.
o Instances of judicial Activism by the Supreme Court include
✓ Directing the Centre to create a new policy to handle drought
✓ Directing the Centre to set up a bad loans panel
✓ Reforming Board for the Control of Cricket in India (a private body)
• Judicial Overreach: There is a very thin line between activism and overreach. Judicial Overreach refers to an extreme form of judicial activism where arbitrary and unreasonable interventions are made by the judiciary into the domain of the legislature or executive. This is a situation where the court encroaches upon the role of the legislature by making laws. Instances of judicial overreach by the Supreme Court include
o Denying the executive any role in the appointment of judges by instituting collegiums (an extra-constitutional body).
o Invalidating the National Judicial Accountability Commission Act, 2014 seeking to ensure transparency and accountability in higher judiciary.
REGULATION OF NGOs IN INDIA
Recently, the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) tightened oversight on funds received by non-governmental organisations (NGOs).
• MHA has laid out a series of guidelines and charter to make NGOs and banks comply with new provisions of the amended Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act, 2010 (FCRA).
• The charter for banks says that “donations received in Indian rupees” by NGOs from “any foreign source even if that source is located in India at the time of such donation” should be treated as “foreign contribution”.
• Also, it stated foreign contribution has to be received only through banking channels and any violation by the NGO or by the bank may invite penal provisions of FCRA.
NGOs and their importance
• NGO is defined by the World Bank as a not-for-profit organization that pursue activities to relieve suffering, promote the interests of the poor, protect the environment, provide basic social services, or undertake community development.
• These organisations are not a part of the government, but have a legal status and are registered as Trust, Society or Private Limited Non-Profit Company.
• Constitutionally NGOs are backed by:
o Article 19(1)(c) which allows the right to form associations,
o Article 43 to promote cooperatives in rural areas,
o Concurrent List mentions charitable institutions, charitable and religious institutions.
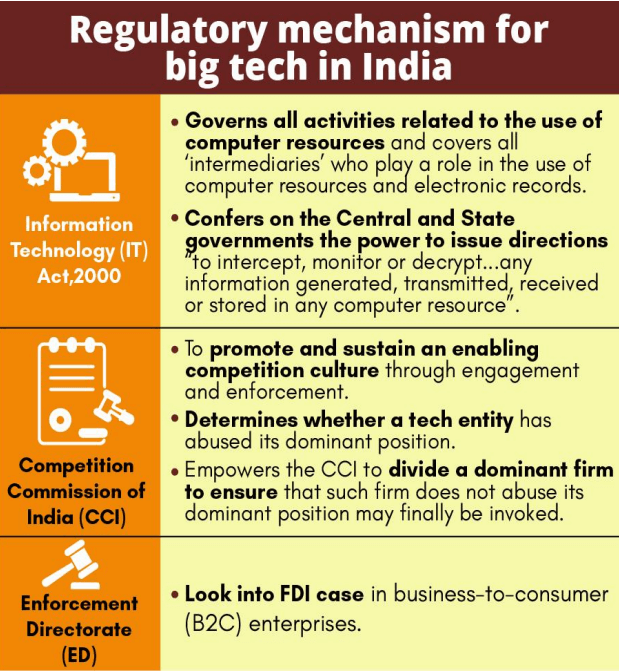
REGULATION OF BIG TECH COMPANIES
There are multiple investigations worldwide going on the abuse of monopolistic power by the Big Tech firms like Facebook, Google etc.
Anti-trust laws
• Antitrust laws are those laws that prevent companies from working together to control prices unfairly or to create a monopoly.
• India’s antitrust law, The Competition Act, 2002, was fully constituted in 2009 replacing the Monopolistic and Restrictive Trade Practices Act of 1969.
• Competition Act monitors any economic activity that monopolizes competition within the market and aims to protect consumers and small enterprises, and ensures the freedom of trade.
• Competition Commission of India has been setup under 2002 act to regulate anticompetitive activity in the country.
ROLE OF INDIAN DIASPORA IN MAKING INDIA SELF-RELIANT
Recently, the 16th Pravasi Bharatiya Divas (PBD) Convention was held virtually in New Delhi with the theme “Contributing to Aatmanirbhar Bharat”.
About Indian Diaspora
• The term ‘diaspora’ is commonly understood to include Non-Resident Indians (NRIs), Persons of Indian Origin (PIOs) and Overseas Citizens of India (OCI), of which PIO and OCI card holders were merged under one category — OCI — in 2015.
• Broadly speaking, for the Indian government, the diaspora encompasses a group of people who can either trace their origins to India or who are Indian citizens living abroad, either temporarily or permanently.
• Status of Indian Diaspora: As per the World Migration Report 2020, India was the leading country of origin of international migrants in 2019 with a 17.5 million strong diaspora.
o In 2018, remittance inflows to India amounted to USD 79 billion, the largest in the world.
About Pravasi Bharatiya Divas (PBD)
• PBD is celebrated once in every two years to strengthen the engagement of the overseas Indian community with the Government of India and reconnect them with their roots.
o PBD is held on January 9 as it was on this day in 1915, Mahatma Gandhi returned to India from South Africa and led the country’s freedom struggle.
o During the PBD convention, select eminent Indian diaspora members are awarded the Pravasi Bharatiya Samman Awards.
GROUP OF SEVEN (G7)
The United Kingdom has invited Prime Minister of India to attend the G7 summit scheduled to be held in June 2021.
• Apart from India, Australia and South Korea are also invited to participate in the proceedings of the summit as guest countries.
• U.K. will use the G7 summit, as the opportunity to build back better from coronavirus.
• Previously, in 2019 India participated in the G7 summit in Biarritz on invitation by France.
About Group of Seven (G7)
• G7 is a bloc of industrialized democracies Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom, and the United States.
• Russia belonged to the forum from 1998 through 2014, when the bloc was known as the Group of Eight (G8), but was suspended following its annexation of Crimea.
• There are no formal criteria for membership, but the participants are all developed democracies.
• The G-7 nations meet annually and presided over by leaders of member countries on a rotational basis to discuss issues such as global economic governance, international security, and energy policy.
PM-KISAN Scheme
• It is a Central Sector Scheme with 100% funding from Government of India.
• Under the scheme Income support of Rs. 6000/- per year is provided to all land holding farmer families across the country, irrespective of land size, in three equal instalments of Rs.2000/- every four months.
o Amount is released by the Central Government directly into the bank accounts of the eligible farmers under Direct Benefit Transfer mode.
• Objective of the scheme is to
o Provide income support to all landholding farmers’ families (irrespective of the landholdings) in the country.
o Supplement financial needs of farmers for procuring various inputs related to agriculture and allied activities as well as domestic needs.
• Farmer’s family is defined as a family comprising of husband, wife and minor children. There are around 11 crore beneficiaries registered under the scheme.
PM FASAL BIMA YOJNA
PM Fasal Bima Yojna (PMFBY) has completed 5 years of its operation.
• PMFBY is a Central Government’s flagship crop insurance scheme launched in 2016 that replaced the earlier two schemes National Agricultural Insurance Scheme and Modified NAIS.
• It aims to provide insurance and financial support to farmers in the event of crop failure and targets to bring 50 per cent of cultivated area under crop insurance to:
o stabilise farmer’s income,
o ensure the flow of credit and
o encourage farmers to innovate and use modern agricultural practices.
Features of the PMFBY
• Coverage of Farmers: All farmers growing notified crops in a notified area during the season who have insurable interest in the crop are eligible.
• Coverage of Crops: State government notifies major crops for the Rabi and Kharif seasons.
• Premium Rates: Farmers pay just 1.5 per cent premium for rabi, 2 per cent premium for kharif and 5 per cent for commercial crops. Balance premium is paid by the state and central governments in equal proportion.
• Area-based Insurance Unit: all farmers in a particular area must pay the same premium and have the same claim payments. The area approach reduces the risk of moral hazard and adverse selection.
• Coverage of Risks: It aims to prevent sowing/planting risks, loss to standing crop, post-harvest losses and localised calamities. The sum insured is equal to the cost of cultivation per hectare, multiplied by the area of the notified crop proposed by the farmer for insurance.
• Innovative Technology Use: It recommends using drones to estimate crop loss; and using mobile phones to reduce delays in claim settlements.
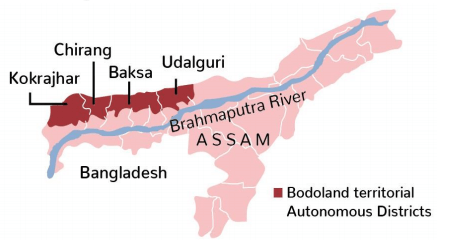
BODO PEACE ACCORD
First anniversary of the 3rd Bodo Peace Accord was celebrated in Assam recently.
About Bodos
• Bodoland is a state demanded by a tribal community called Bodos in Assam, who comprise of 5%-6% of the state’s population.
• They are single largest tribal community in Assam.
• It consists of regions located extreme north of north bank of Brahmaputra river in the state of Assam, by the foothills of Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh.
About 3rd Bodo Peace Accord
• 3rd Bodo Peace Accord as tripartite agreement between the Centre, Assam Governmen and the banned Assam- based insurgent group National Democratic Front of Bodoland (NDFB) was signed on 27th January 2020, for bringing a lasting peace in Bodo-dominated areas in Assam.
Key highlights of the accord
o Bodo Territorial Areas District (BTAD) was reorganized by including new Bodo-dominated villages contiguous to the existing BTAD and excluding villages with a predominantly non-tribal population.
o BTAD renamed as Bodoland Territorial Region with more executive, administrative, legislative and financial powers.
o A commission, headed by a neutral person and represented by stakeholders, will be constituted by the central government for the demarcation and reorganisation of the BTR
o Bodos living in hills districts of Karbi Anglong and Dima Hasao would be conferred Scheduled Hill Tribe status.
o Number of seats in Bodoland Territorial Council will be increased from 40 to 60.
o Bodo with Devnagri script would be associate official language for entire Assam.
o Deputy Commissioners and Superintendents of Police will be posted in consultation with the Chief Executive Member (CEM) of the BTC.
o A Special Development Package of Rs. 1500 crores over three years were provided.
E-WASTE
As per report of Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB), India collected just 10% e-waste in 2018-19 and 3.5% in 2017-18 out of total generated waste.
About E-waste
• Electronic waste (e-waste), refers to all items of electrical and electronic equipment (EEE) and its parts that have been discarded by its owner as waste without the intent of re-use.
o EEE includes a wide range of products with circuitry or electrical components with a power or battery supply
o The biggest contributors to the level of e-waste at present are household appliances such as irons, vacuum cleaners, washing machines and fridges. But the rapidly-growing “Internet of things” – internet-connected gadgets – is expected to generate e-waste at a faster rate, as connectivity becomes embedded into everyday items.
About the Basel Convention
• The Basel Convention on the Control of Trans-boundary Movements of Hazardous Wastes and Their Disposal is a multilateral treaty aimed at suppressing environmentally and socially detrimental hazardous waste trading patterns.
o It was adopted in 1989 and it came into force in 1992 and, to date, has been signed by 187 countries. India became a party to the Basel Convention in 1992.
• Basel Convention obliges its Parties to ensure that such wastes are managed and disposed of in an environmentally sound manner.
o E-waste, due to its constitution, often contains hazardous elements.
ANTARCTIC OZONE HOLE
According to World Meteorological Organization (WMO), Antarctic ozone hole — one of the deepest, largest in the last 40 years — has closed.
• The formation of ozone hole in the Antarctic has been an annual occurrence and has been recorded for the last 40 years.
• This year, ozone hole over Antarctic had rapidly grown from mid-August and peaked in early October 2020.
• This time around, expansion of the hole was driven by a strong, stable and cold polar vortex, which kept the temperature of the ozone layer over Antarctica consistently cold.
• This prevented the mixing of ozone depleted air above Antarctica with ozone rich air from higher latitudes.
About ozone hole
• Ozone layer is the common term for the high concentration of ozone that is found in the stratosphere (layer of the atmosphere between around 10-50 km altitude).
o Atmospheric ozone absorbs ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun, particularly harmful UVB-type rays.
• Ozone hole refers to a region in stratosphere where concentration of ozone becomes extremely low.
Effects of ozone depletion for humans and the environment
• Ozone layer depletion causes increased UV radiation levels at the Earth’s surface, which is damaging to human health. Negative effects include
o increases in certain types of skin cancers, eye cataracts and immune deficiency disorders.
o UV radiation also affects terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems, altering growth, food chains and biochemical cycles.
o Aquatic life just below water’s surface is particularly adversely affected by high UV levels.
o UV rays also affect plant growth, reducing agricultural productivity.
International Treaties and Cooperation about the Protection of the Stratospheric Ozone Layer
• Adopted in 1985, The Vienna Convention for the Protection of the Ozone Layer is the precursor to the Montreal Protocol. It is often called a framework convention, because it served as a framework for efforts to protect the globe’s ozone layer.
• Montreal Protocol (1987) on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer regulates production and consumption of nearly 100 ozone depleting substances (ODS).
• The Kigali Amendment (2016) to Montreal Protocol extended controls to phase down the production and consumption of hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) because these substances are powerful greenhouse gases.
• United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) Ozone Secretariat to implement the Montreal protocol.
TRANS FATS
After oils, FSSAI has put the cap on trans fats in foods.
• Recently, FSSAI issued a revised regulation according to which “Food products” using edible oils and fats as an ingredient shall not contain industrial TFAs more than 2% by mass of total oils/fats present in product, on and from 1st January, 2022.
• Earlier, in December, FSSAI had capped the amount of trans fatty acids (TFA) in ‘oils and fats’ to 3% for 2021 and 2% by 2022 from the current permissible limit of 5% through an amendment to the Food Safety and Standards (Prohibition and Restriction on Sales) Regulations.
• Trans fat, or trans-fatty acids, are unsaturated fatty acids that come from either natural or industrial sources:
o Naturally occurring trans-fat come from ruminants (cows and sheep).
o Industrially produced trans-fat are formed in an industrial process that adds hydrogen to vegetable oil converting the liquid into a solid, resulting in “partially hydrogenated” oil (PHO).
• Industrially produced trans-fats are found in hardened vegetable fats such as margarine and ghee (clarified butter) and are often present in snack foods, baked goods and fried foods.
• Manufacturers often use them as they have a longer shelf life and are cheaper than other fats.
• They are more unhealthy than saturated fats as they increase bad cholesterol, i.e., Low Density Lipoproteins (LDL) and lower good cholesterol, i.e., High Density Lipoproteins (HDL).
Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI)
• It has been established under Food Safety and Standards, 2006 which consolidates various acts & orders that have hitherto handled food related issues in various Ministries and Departments.
• FSSAI has been created for laying down science-based standards for articles of food and to regulate their manufacture, storage, distribution, sale and import to ensure availability of safe and wholesome food for human consumption.
• Ministry of Health & Family Welfare is the Administrative Ministry for the implementation of FSSAI.
INDIA INNOVATION INDEX 2020
Recently, NITI Aayog has released the second edition of the India Innovation Index.
About the Index
• It seeks to scrutinize the innovation capacities and performance of Indian states. The first edition of the index was launched in 2019.
• It provides an extensive framework for the constant evaluation of the innovation ecosystem of Indian states and UTs.
• The index intends to accomplish the following three functions:
o Rank all states and UTs based on their index score.
o Identify opportunities and challenges.
o Assist in modifying governmental policies to foster innovation.
• Index measures innovation inputs through ‘Enablers’ and innovation output as ‘Performance.
o Enabler parameters (factors that reinforce innovative capacities): Human Capital, Investment, Knowledge Workers, Business Environment, Safety and Legal Environment.
o Performance parameters: Knowledge Output, Knowledge Diffusion.
• The states have been bifurcated into three categories:
o Major states: Top performers are Karnataka, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Telangana.
o North-east and hill states: Top performers are Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Manipur.
o UTs and City States: Top performers are Delhi, Chandigarh, Daman and Diu.
India and Innovation
• Innovation is the creation, development and implementation of a new product, process or service, with the aim of improving efficiency, effectiveness or competitive advantage.
• India ranks 48th in Global Innovation Index (GII) 2020.
o GII is a joint collaborative effort between the WIPO, Cornell University, and INSEAD that annually ranks the innovation performance of more than 130 economies.
• Additionally, India ranks the highest amongst central and southern Asian countries and is a new entrant to the Top 3 innovation economies among the lower-middle-income group nations with Vietnam and Ukraine.
NETAJI SUBHAS CHANDRA BOSE
On 23rd January, 2021, India celebrated the 125th birth anniversary of Netaji Subhas Chandra Bose as ‘Parakram Divas.
His military activities during World War II
o After reaching Germany in 1942, he started ‘Azad Hind Radio’ and established ‘Free India Centre’ (a precursor of the Azad Hind Government).
o He arrived in Singapore in July 1943 and took charge of the Indian National Army (INA) or Azad Hind Fauj and expanded it to three divisions. INA was established by Mohan Bose. Rash Behari Bose, a veteran nationalist exiled in Japan came to aide Netaji.
o In Singapore, he formed an Indian government-in-exile ‘the Azad Hind Government’. This provisional government also had its own currency, court, civil code, Army (the INA) and national anthem.
o In 1943, as the Head of the State of the Provisional Government, he declared war on Britain for the liberation of India.
o The INA under the clarion call of “Chalo Delhi” reached Moirang in Manipur and shook the British confidence.
✓ The INA was able to win back Rangoon, Imphal and Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
✓ Netaji renamed Andaman and Nicobar (A&N) Island as Shaheed and Swaraj. In 2018, the Ross Island, Neil Island and Havelock Island of (A&N) Islands were renamed as Netaji Subhas Chandra Bose Dweep, Shaheed Dweep and Swaraj Dweep respectively.
o The great salutation every Army personnel uses today, ‘Jai Hind’, was coined by Netaji’s aide Abid Hasan.
PRABUDDHA BHARAT JOURNAL
Recently, Prabuddha Bharata journal celebrated its 125th anniversary.
About Prabuddha Bharata
• Prabuddha Bharata or Awakened India is an English-language monthly journal of the Ramakrishna Mission.
• Prabuddha Bharata was founded in 1896 by P. Aiyasami, B. R. Rajam Iyer, G. G. Narasimhacharya, and B. V. Kamesvara Iyer, in Madras (now Chennai), at the behest of Swami Vivekananda.
• It is the “longest-running” monthly English magazine of the country.
• It carries articles on social sciences and humanities comprising historical, psychological, cultural and social sciences themes.
• Luminaries like Netaji Subhas Chandra Bose, Bal Gangadhar Tilak, Sister Nivedita, Sri Aurobindo, Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan etc. wrote in the journal.
INCLUSION OF INDIGENOUS SPORTS IN KHELO INDIA YOUTH GAMES 2021
Recently, Sports Ministry has approved the inclusion of four Indigenous Games to be a part of Khelo India Youth Games (KIYG) 2021. The games include: Gatka, Kalaripayattu, Thang-Ta and Mallakhamba, along with Yogasana.


HENLEY PASSPORT INDEX 2021
• Henley Passport Index is the ranking of all the world’s passports according to the number of destinations their holders can access without a prior visa.
• Ranking is based on exclusive data from the International Air Transport Association (IATA) and ranks 199 passports in total.
o IATA maintains the world’s largest and most accurate database of travel information.
• Japan ranks first on the index with passport holders able to access 191 destinations around the world visa-free.
MILITARY EXERCISES
• Exercise Kavach: It is a joint Military exercise involving assets of Indian Army, Indian Navy, Indian Air Force and Indian Coast Guard.
• Desert Knight-21: It is a bilateral Air exercise between Indian Air Force and French Air and Space Force.
AKASH-NG MISSILE
• Recently, Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) successfully conducted the maiden test of the New Generation Akash missile (Akash-NG).
• Akash-NG is a new generation Surface to Air Missile meant for use by Indian Air Force with an aim of intercepting high manoeuvring low RCS (Radar Cross Section) aerial threats.
ASMI
• It is India’s first indigenous 9mm Machine Pistol that has been jointly developed by DRDO and Indian Army.
o 3D Printing process has been used in designing and prototyping of various parts.
• It can be used as personal weapon for heavy weapon detachments, commanders, tank and aircraft crews, drivers/dispatch riders, radio/radar operators, Closed Quarter Battle etc.
TRADITIONAL KNOWLEDGE DIGITAL LIBRARY
• Traditional Knowledge Digital Library (TKDL) is an Indian digital knowledge repository of traditional knowledge (TK), especially about medicinal plants and formulations used in Indian systems of medicine.
o TK is knowledge, know-how, skills and practices that are developed, sustained and passed on from generation to generation within a community, often forming part of its cultural or spiritual identity.
• TKDL was initiated in 2001, as a collaboration between the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), Ministry of S&T, and Department AYUSH, Ministry of Health.
o TKDL database contains more than 3.9 lakh formulations/ practices from the Indian systems of medicine (Ayurveda, Yoga, Siddha, Unani and Sowa Rigpa)in digitized format in five languages: English, German, French, Japanese and Spanish.
• It seeks to prevent misappropriation of the country’s traditional medicinal knowledge at International Patent Offices by preventing the granting of patents for products developed utilizing Indian TK.
o Also, non-patent database serves to foster modern research based on traditional knowledge, by simplifying access to vast knowledge of practices.
RISA
• Risa is a handwoven cloth used as a female upper garment, and also as headgear by the Tripura’s indigenous communities
o It is being branded under the India Handloom Brand as a signature identity of the state.
• Traditional Tripuri female attire comprises three parts — risa, rignai and rikutu.
o Rignai is primarily worn as the lower garment. It can be understood as an indigenous variety of the sari.
o Rituku is mainly used as a wrap, or like a ‘chunri’ or a ‘pallu’ of the Indian saree.
VANADIUM
• For the first time a promising concentration of vanadium is found in the Depo and Tamang (Arunachal Pradesh).
• Vanadium in its pure form is a soft, grey and ductile element primarily derived from mined iron ore, carbonaceous shale or phyllites and steel slag.
o The largest deposits are in China, followed by Russia and South Africa.
• Vanadium alloys are durable in extreme temperature and environments, and are corrosion-resistant. Hence, used in steel, vanadium redox batteries, etc.
