INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY (INTERMEDIARY GUIDELINES AND DIGITAL MEDIA ETHICS CODE) RULES, 2021
• In December 2018, the Supreme Court (SC) in suo-moto writ petition (Prajjawala case) had observed that Centre may frame necessary guidelines to eliminate child pornography, rape and gangrape imageries, videos and sites in content hosting platforms and other applications.
• Subsequently, MeitY prepared the draft Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines) Rules 2018 to replace the rules notified in 2011 to strengthen the legal framework and make the social media platforms accountable under the law.
• In October 2020, the SC had sought the Centre’s response on a Public Interest Litigation (PIL) for regulating Over-the-top (OTT) by an autonomous body.
• In November 2020 the Union government brought OTT platforms and news and current affairs content on online platforms under the ambit of the I&B ministry.
• In February 2021 the SC issued a notice to the Central Government seeking creation of a proper board, institution or association for managing and monitoring OTT, streaming and media platforms.
• Rules 2021 has been framed by the Central Government in exercise of powers under section 87 (2) of the Information Technology Act, 2000
GUIDELINES RELATED TO SOCIAL MEDIA INTERMEDIARIES
Key provisions
• Due diligence to be followed by intermediaries: Rules prescribe due diligence that must be followed by social media intermediaries like retention of user information for a period of 180 days, reporting cyber security incidents etc.
o In case, due diligence is not followed by the intermediary, safe harbour provisions will not apply to them.
o These safe harbour provisions have been defined under Section 79 of the IT Act, and protect social media intermediaries by giving them immunity from legal prosecution for any content posted on their platforms.
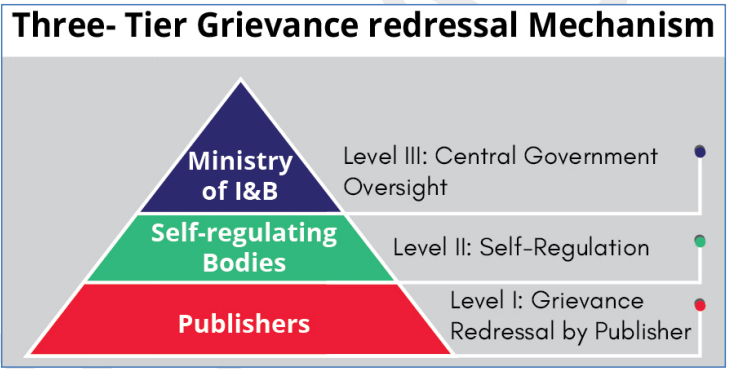
• Grievance Redressal Mechanism: Intermediaries shall appoint a Grievance Officer to deal with complaints and share the name and contact details of such officer.
o Grievance Officer shall acknowledge the complaint within 24 hours and resolve it within 15 days from its receipt.
• Ensuring Online Safety and Dignity of Users, especially Women Users: Intermediaries shall remove or disable access within 24 hours of receipt of complaints of contents that exposes the private areas of individuals or is in the nature of impersonation including morphed images etc.
GUIDELINES RELATED TO DIGITAL MEDIA AND OTT PLATFORMS
Key provisions
• Rules establish a soft-touch self-regulatory architecture and a Code of Ethics and three tier grievance redressal mechanism for news publishers and OTT Platforms and digital media. They have been notified under section 87 of IT Act empowering the I&B Ministry to implement this part of the Rules which prescribe the following:
Code of Ethics
• As applicable to OTT platforms:
o OTT platforms, called as the publishers of online curated content in the rules, would self-classify the content into five age-based categories- U (Universal), U/A 7+, U/A 13+, U/A 16+, and A (Adult) based on factors such as themes and messages, violence, nudity, drug and substance abuse etc.
o Platforms would be required to implement parental locks for content classified as U/A 13+ or higher, and reliable age verification mechanisms for content classified as “A”.
SEDITION LAW IN INDIA
Supreme Court rejected a plea urging it to re-examine the constitutional validity of Section 124A of IPC, which deals with sedition.
Background
• The law was originally drafted in 1837 by Thomas Macaulay, the British historian-politician, but was inexplicably omitted when the IPC was enacted in 1860.
• Section 124A was inserted in 1870 by an amendment introduced by Sir James Stephen.
• Bal Gangadhar Tilak, Annie Besant, the Ali Brothers, Maulana Azad, Gandhi and very many others suffered imprisonment under this law.
About Sedition
• Indian Penal Code defines sedition (Section 124A) as an offence committed when any person brings or attempts to bring into hatred or contempt, or excites or attempts to excite disaffection towards the government established by law in India by:
o words, either spoken or written
o signs
o visible representation, or otherwise
• ‘Disaffection’ includes disloyalty and all feelings of enmity. However, comments without exciting or attempting to excite hatred, contempt or disaffection do not constitute an offence under this section.
It is a non-bailable offence. Punishment ranges from imprisonment up to 3 years to a life term, to which fine may be added.
• A person charged under this law is barred from a government job. They have to live without their passport and must produce themselves in the court at all times as and when required.
Supreme Court judgement on sedition law
• The constitutionality of sedition was challenged in the Supreme Court in Kedar Nath Vs State of Bihar (1962).
• The Court upheld the law on the basis that this power was required by the state to protect itself.
o However, it had added a vital caveat that “a person could be prosecuted for sedition only if his acts caused incitement to violence or intention or tendency to create public disorder or cause disturbance of public peace”.
• In Balwant Singh v. State of Punjab (1995), Supreme Court had clarified that merely shouting slogans does not amount to sedition.
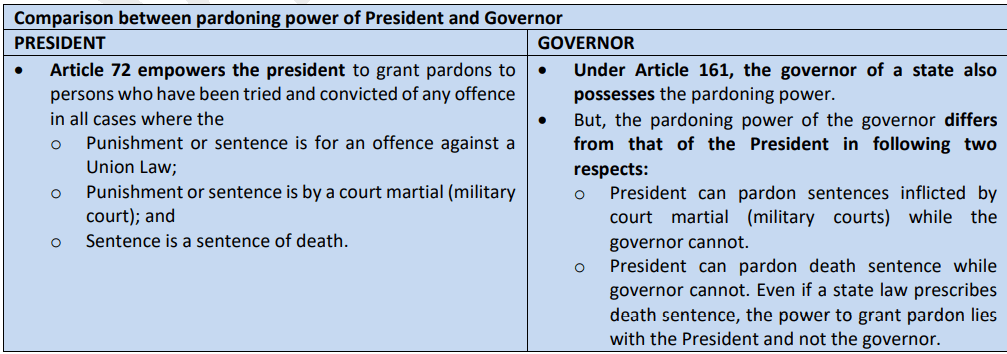
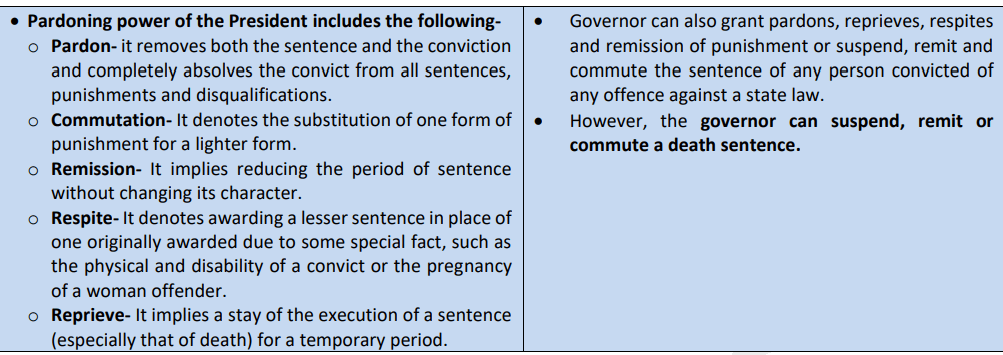
PARDONING POWER OF PRESIDENT AND GOVERNOR
REGISTERED UNRECOGNIZED PARTIES
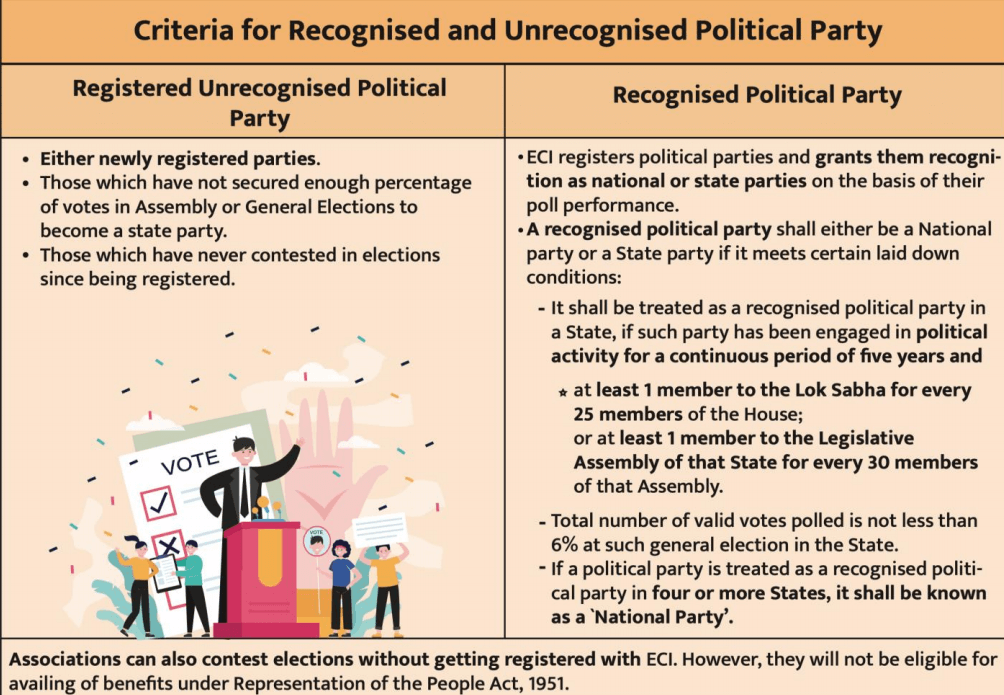
Benefits of recognized political party
• Exclusive allotment of election symbols to the candidates fielded by the party. A RUPP can select a symbol from a list of free symbols.
• Need only one proposer for filing the nomination.
• Entitled for two sets of electoral rolls free of cost.
• Get broadcast/telecast facilities over Akashvani/Doordarshan during general elections.
• Can have a maximum of 40 Star campaigners and a RUPP can nominate a maximum of 20 Star Campaigners.
• Eligible for subsidized lands for party offices.
ARBITRATION AND CONCILIATION (AMENDMENT) BILL, 2021
Recently, Parliament passed the Arbitration and Conciliation (Amendment) Bill, 2021.
Background
• The Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996 was enacted with a view to consolidate and amend the law relating to domestic arbitration, international commercial arbitration, enforcement of foreign arbitral awards and the law relating to conciliation.
• Further, the act was amended in 2015, to make arbitration process user friendly, cost effective and ensure speedy disposal and neutrality of arbitrators.
• It was again amended in 2019 to promote institutional arbitration in the country.
• Arbitration and Conciliation (Amendment) Ordinance, 2020 was brought to ensure that all the stakeholder parties get an opportunity to seek unconditional stay of enforcement of arbitral awards.
Key features of the bill:
o Automatic stay on awards: Bill clarifies that a stay on the arbitral award may be granted by the Court, even during the pendency of the setting aside application, if it is prima facie satisfied that the elevant arbitration agreement was induced by fraud or corruption.
o Qualifications of arbitrators: Bill removes 8th Schedule for arbitrators and states that the qualifications, experience, and norms for accreditation of arbitrations will be specified under the regulations by Arbitration Council of India (ACI).
About Arbitration Council of India (ACI)
• Arbitration and Conciliation (Amendment) Act 2019 seeks for the establishment and incorporation of an independent body namely, Arbitration Council of India (ACI).
• ACI is set for grading of arbitral institutions and accreditation of arbitrators.
• ACI will be headed by a Chairperson, who has been a Judge of the Supreme Court or a Chief Justice or Judge of a High Court or an eminent person appointed by central government in consultation with the Chief Justice of India.
INDIA – MAURITIUS
India and Mauritius signed Comprehensive Economic Cooperation and Partnership Agreement (CECPA).
About CECPA
• CECPA is the first trade agreement signed by India with a country in Africa.
• Agreement is a limited agreement, which will cover Trade in Goods, Rules of Origin, Trade in Services, Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT), Sanitary and Phytosanitary (SPS) measures, Dispute Settlement, Movement of Natural Persons, Telecom, Financial services, Customs Procedures and Cooperation in other Areas.
Other types of trade agreements
• Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA): India has signed CEPA with Japan, Sri Lanka, and South Korea
o The CEPA is a bilateral agreement that covers trade in goods and services, investment, competition and intellectual property rights (IPRs).
o The pact seeks to abolish import duties on most products, increase access for Indian professionals and contractual service suppliers to signing countries and liberalise investment rules.
• Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA): India signed CECA with Malaysia, Singapore, and Thailand.
o CECA, as an integrated package, consisting of the following agreements:
✓ Free Trade Agreement, which would include inter-alia, trade in goods and services, and investment
✓ bilateral agreement on investment promotion, protection, and cooperation;
✓ improved Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement
✓ liberal Air Services Agreement, and Open Skies for Charter Flights
✓ work programme of cooperation in a number of areas including health care, education, media, tourism etc.
• Free Trade Agreement (FTA): FTA between two or more countries reduces barriers to imports and exports among them. This is provided through preferential trade terms, tariff concession etc.
• Preferential Trade Agreement (PTA): This is unilateral trade preferences, include Generalized System of Preferences schemes under which developed countries grant preferential tariffs to imports from developing countries
o Tariffs may be reduced at low or zero for some products.
Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA)
• It is tax treaty between two or more countries to avoid taxing the same income twice is known as DTAA.
o Double taxation is the levy of tax by two or more countries on the same income, asset or financial transaction.
• Under DTAA there are agreed rates of tax and jurisdiction on specified types of income arising in a country.
• When a tax-payer resides in one country and earns income in another country, he is covered under DTAA, if those two countries have DTAA in place.
MILITARY COUP IN MYANMAR
Recently, Myanmar (formerly called Burma) military grabbed power in a coup, third time in the nation’s history since its independence from British rule in 1948.
• Military (also called Junta and Tatmadaw) has alleged that the general elections held in November 2020 were full of irregularities and that therefore, the results are not valid.
o In 2020 elections, Aung San Suu Kyi led the National League for Democracy (NLD) to a landslide win.
• Military had demanded that the United Elections Commission of Myanmar, or the government, or outgoing parliamentarians prove at a special session before the new parliament convenes, that elections were free and fair.
NEW START NUCLEAR ARMS TREATY
Recently, United States (US) has extended the New START (Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty) nuclear arms control treaty with Russia for five years.
• New START treaty is the last remaining arms reduction pact between US and Russia.
• The treaty, which first went into effect in 2011, limits U.S. and Russia to deploying no more than 1,550 strategic nuclear warheads each and imposes restrictions on the land- and submarine-based missiles and bombers to deliver them.
EXTRADITION
Recently, UK court paved way for Nirav Modi to be extradited to India.
• Fugitive jeweller Nirav Modi is wanted by Central Bureau of Investigation and Enforcement Directorate in Rs. 13,500-crore bank loan fraud case.
o India-UK Extradition Treaty was signed in 1992
FIFTEENTH FINANCE COMMISSION REPORT
The Fifteenth Finance released its report which was recently tabled in the Parliament.
About the Fifteenth FC
• The Commission was chaired by Mr. N.K. Singh and the report was titled ‘Finance Commission in COVID times.’
• The Commission was required to submit two reports. The first report, consisting of recommendations for the financial year 2020-21. The final report with recommendations for the 2021-26 period.
o Also, this is also the first ever Commission to have given recommendations spanning a period of six years, that is, 2020-26.
• The Commission was asked to prepare a report on a many new and unique demand via its Terms of Reference (ToR).
How the Terms of Reference (ToR) of Fifteenth FC were different from previous commissions?
• Fiscal Consolidation Roadmap: The Commission was asked to review the current finances of both state and central government and recommend a fiscal consolidation roadmap for sound fiscal management.
o This task became all the more difficult with the outbreak of the Pandemic, as the need for fiscal room became dire.
• Indirect Taxation System: The commission was asked to evaluate the impact of the GST, including the need for payment of compensation for possible loss of revenues for 5 years, and abolition of a number of cesses.
• Measurable Performance Incentives: The Commission was asked to consider proposing of measurable performance-based incentives for States, at the appropriate level of government in areas like deepening of tax nets, population control, power sector reforms etc.
• Using 2011 population against 1971 population data: The Commission had to use the population data of 2011 while making its recommendations. This was tricky as there was an active opposition from Southern States on usage 2011 population data.
• Other unique demands:
o Analyzing the possibility of creation of a non-lapsable defense fund.
o Reviewing the present arrangements on financing Disaster Management initiatives.
What are the recommendations given by the Fifteenth FC Report for 2021-26 period?
Vertical Devolution:
The commission has recommended maintaining the vertical devolution at 41%.
• The idea is to maintain the same level of devolution as recommended by 14th FC (i.e., 42%), the adjustment of about 1% has been made due to the changed status of the erstwhile State of Jammu and Kashmir into the new Union Territories of Ladakh and Jammu and Kashmir.
• Gross tax revenue for 5-year period is expected to be 135.2 lakh crore. Out of that, Divisible pool (after deducting cesses and surcharges & cost of collection) is estimated to be 103 lakh crore.
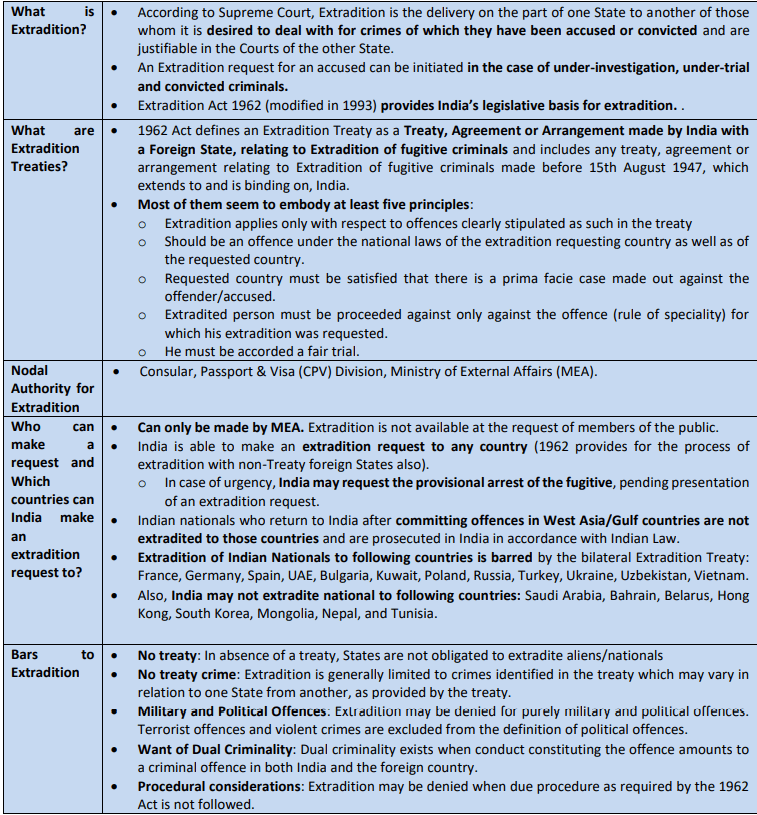
Horizontal Devolution:
• The horizontal devolution is primarily based on three principles namely need of states, equity among states and performance of states. To balance all three principles, six criteria are used to calculate tax distribution- Income Distance, Area, Population (2011), Demographic Performance, Forest and Ecology and Tax and Fiscal Transfers.
Grants to States
• Revenue deficit grants: 17 states will receive grants worth Rs 2.9 lakh crore to eliminate revenue deficit.
• Sector-specific grants: Sector-specific grants of Rs 1.3 lakh crore will be given to states for sectors like health, education, implementation of agricultural reforms etc. A portion of these grants will be performance-linked.
• State-specific grants: The Commission recommended state-specific grants of about 0.5 lakh crore. These will be given in the areas of social needs, administrative governance and infrastructure etc.
• Grants to local bodies: The total grants to local bodies will be Rs 4.36 lakh crore (a portion of grants to be performance-linked).
o Grants to local bodies (other than health grants) will be distributed among states based on population and area, with 90% and 10% weightage, respectively.
o Also, no grants will be released to local bodies of a state after March 2024 if the state does not constitute State Finance Commission and act upon its recommendations by then.
DRAFT BLUE ECONOMY POLICY FOR INDIA
Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) has rolled out the Draft Blue Economy policy for India in the public domain inviting suggestions and inputs from various stakeholders including industry, NGOs, academia, and citizens.
About Blue Economy
• According to World Bank, Blue Economy refers to sustainable use of ocean resources for economic growth, improved livelihood and jobs, and ocean ecosystem health.
• Blue Economy seeks to promote economic growth, social inclusion and the preservation or improvement of livelihoods as well as ensuring environmental sustainability of the oceans and coastal areas.
• The economic philosophy of the Blue Economy was first introduced in 1994 by Professor Gunter Pauli at the United Nations University (UNU) to reflect the needs of future growth and prosperity, along with the threats posed by global warming.
Placer deposits
• It is an accumulation of valuable minerals formed by gravity separation from a specific source rock during sedimentary processes.
• India is rich in Placer minerals like nickel, uranium, copper, thorium, titanium, poly metallic sulphides, poly metallic manganese nodules, coastal ilmenite, garnet and zircon etc.
• Polymetallic nodules and polymetallic massive sulphides are the two mineral resources of commercial interest to developers in the Indian Ocean.
o Typically found at 4 to 5 km in water depth, polymetallic nodules are golf-to-tennis ballsized nodules containing nickel, cobalt, iron, and manganese that form over millions of years on the sediment of the seafloor.
COMPANIES (CORPORATE SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY (CSR) POLICY) AMENDMENT RULES, 2021
Recently, Ministry of Corporate Affairs brought into effect the Companies (CSR Policy) Amendment Rules, 2021 by amending amend the Companies (CSR Policy) Rules, 2014.
About Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
• It is a management concept whereby companies integrate social and environmental concerns in their business operations and interactions with their stakeholders.
• In 2013, Companies Act 2013 introduced changes with respect to company formation, administration, and governance, and incorporated an additional section i.e. Section 135 on CSR obligations for companies listed in India.
o With this, India became the first country to legislate CSR activities under Companies Act 2013.
• Every qualifying company requires spending of at least 2% of its average net profit (Profit before taxes) for the immediately preceding 3 financial years on CSR activities in India.
• Companies applicable to
o annual turnover of 1,000 crore and more or
o net worth of Rs. 500 crore and more or
o net profit of Rs. 5 crore and more.
• CSR is also applicable to branch and project offices of a foreign company in India.
• Various CSR activities includes:
o eradicating extreme hunger and poverty,
o promotion of education, promoting gender equality and empowering women,
o reducing child mortality and improving maternal health ensuring environmental sustainability,
o employment enhancing vocational skills,
o social business projects

ASSET RECONSTRUCTION COMPANY (ARC)
Union budget 2021-22 has proposed a new ARC/Bad Bank to consolidate and take over existing bad loans.
About the Proposal
• The ARC/bad bank proposed in the Budget will be set up by banks (both state-owned and private sector banks), and there will be no equity contribution from the government.
o However, the Government may provide sovereign guarantee that could be needed to meet regulatory requirements.
• It will have an Asset Management Company (AMC) to manage and sell bad assets.
o AMC manages funds for individuals and companies. They make well-timed investment decisions on behalf of their clients to grow their finances and portfolio.
• It will look to resolve stressed assets of Rs. 2-2.5 lakh crore that remain unresolved in around 70 large accounts.
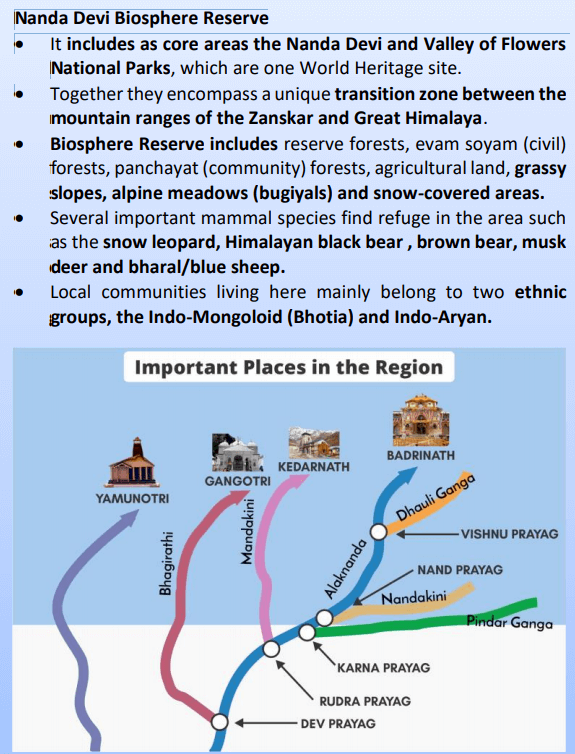
NANDA DEVI GLACIER
Recently, a portion of the Nanda Devi glacier broke of near Joshimath in Uttarakhand’s Chamoli district, and caused an avalanche in the Alaknanda river system (Dhauli Ganga, Rishi Ganga and Alaknanda rivers).
• While scientists are still investigating the cause of the floods, early findings reveal that a major rock/ice avalanche detached itself from a north facing slope northeast of Trisul Peak in the Nanda Devi mountain.
• A study by scientists at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bengaluru, also points to the role of subglacial lakes.
About Glacial lake outburst flood (GLOF)
• A glacier is a large, perennial accumulation of crystalline ice, snow, rock, sediment, and often liquid water that originates on land and moves down slope under the influence of its own weight and gravity.
• GLOF occurs from unstable natural dam formed from glacier retreat.
o When glacier retreats it leaves behind large impression in ground filling it with water and lake is formed, this is known as moraine which can be impunded by pile of debris & ice.
• If the boundaries of these lakes are breached, it can lead to large amounts of water rushing down to nearby streams and rivers, gathering momentum on the way by picking up sediments, rocks and other material, and resulting in flooding downstream.
• GLOFs are generally triggered by an avalanche in the area, construction, anthropological activities, earthquakes, rapid slope movement into the lake etc.
About Nanda Devi Glacier
• Glacier dwells on the Nanda Devi peak which is the second-highest mountain in the country after Kanchenjunga.
• Nanda Devi group of glaciers fall within the upper Rishi Ganga catchment,central Himalaya, covering 690 sq km.
o Nanda Devi Group of Glaciers refers to the cluster of glaciers namely Bethartoli, Kururntoli, Nanda Devi North, Nanda Devi South, Nandakna, Raunth Bank, Dakshini Rishi Bank, Trishul.
• It is a part of the Garhwal Himalayas and is located in Chamoli district of Uttarakhand, between the Rishiganga valley on the west and the Goriganga valley on the east.
• The glacier is located within the Nanda Devi Sanctuary and drains west into the Rishiganga.
GEOTHERMAL ENERGY
An agreement for establishing India’s first-ever geothermal field development project in Leh has been signed.
• The power project known as Geothermal Field Development Project will be established at Puga village of eastern Ladakh. Puga has been identified as the hotspot of geothermal energy in the country (potential of more than 100 mw of geothermal energies.)
• It is to be developed by ONGC Energy, Ladakh Autonomous Hill Development Council, and Power Department of UT Ladakh.
What is Geothermal Energy?
• Geothermal energy is the thermal energy generated and stored inside the Earth’s crust. Geothermal power is the electricity generated from the heat source within the earth’s crust.
• This geothermal energy originates from the geological processes during formation of the planet, radioactive decay of minerals, and from solar energy absorbed at the surface.
Geothermal energy in India
• GSI (Geological Survey of India) has identified 350 geothermal energy locations in the country which have a potential of 10000 MW GE power.
• There are seven geothermal provinces in India: Himalayas – Ladakh, Manikaran, Tapoban; Sohana – Haryana, Rajasthan; West coast – Maharashtra; Cambay – Khambet; Son-Narmada-Tapi (SONATA) – Tatapani, AnhoniSamoni; Godavari – Manuguru; Mahanadi – Bakreshwar
PROTECTION OF CHILDREN FROM SEXUAL OFFENCES (POCSO) ACT, 2012
Recently, the single-judge bench of the Bombay High Court (HC) set aside charges of sexual assault under POCSO Act against a man accused of molesting a 12 year old girl child.
• The Bombay HC absolved an accused from the charges under POCSO Act and instead chose to apply Section 354 of the IPC.
• The High Court judge held that mere groping without “skin-to-skin contact” cannot be termed as sexual assault under the POCSO Act.
• The phrase “skin-to-skin contact” is not mentioned under the POCSO Act.
• The Supreme Court has stayed the order as it was “likely to set a dangerous precedent”.
About POCSO Act, 2012
• It is a comprehensive law for the protection of children (under the age of 18) from the offences of sexual assault, sexual harassment and pornography.
o UN Convention on the Rights of the Child, 1989 (ratified by India in 1992) requires sexual exploitation and sexual abuse to be addressed as heinous crimes.
• It incorporates child-friendly mechanisms at every stage of the judicial process which include reporting, recording of evidence, investigation and speedy trial of offences through designated Special Courts.
• It also mandates that the investigation in the cases is to be completed in two months and trial in 6 months. For this purpose Fast Track Special Courts (FTSCs) are established.
• It also punishes criminals who are in positions of trust of authority like public servants, staff of educational institutions, police etc.
• In 2019 the Act was amended to includes following provisions
o Increases the minimum punishment (including death penalty) for penetrative sexual assault, aggravated penetrative sexual assault.
o Assault resulting in death of child, and assault committed during a natural calamity, or in any similar situations of violence are covered as Aggravated penetrative sexual assault.
o Defines child pornography as any visual depiction of sexually explicit conduct involving a child including photograph, video, digital or computer generated image indistinguishable from an actual child.
NASA’S MARS 2020 PERSEVERANCE ROVER MISSION
National Aeronautics and Space Administration’s (NASA) Perseverance Rover successfully touched down on Mars.
About NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance Rover mission
• Mars 2020 Perseverance Rover mission is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet-Mars.
o It was launched in July 2020.
o Mission seeks signs of ancient life and collect samples of rock and regolith (broken rock and soil) for possible return to Earth.
• Perseverance rover will begin its two-year-long investigation in Jezero Crater to assess the geology and past climate of the Red planet.
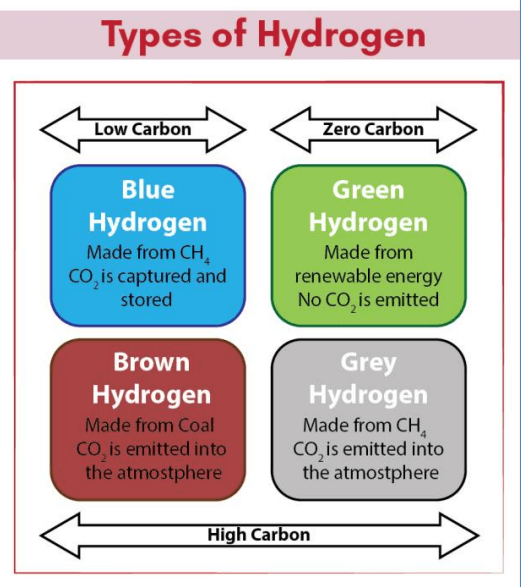
NATIONAL HYDROGEN ENERGY MISSION
Recently, the National Hydrogen Energy Mission was formally announced in the Union budget for 2020-21.
About the mission
• The mission emphasizes on generating hydrogen from green power resources (known as green hydrogen) and enabling its commercial use.
ANCIENT BUDDHIST MONASTERY
900 years old Ancient Buddhist monastery was recently unearthed by Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) in Sitagarhi Hills, Hazaribagh district of Jharkhand.
• It is a 10th century structure resembling a small ‘Buddha Vihar’ (Buddhist shrinecum-monastery).
o Among large monasteries, Nalanda was the first and the most extensive monastery in ancient India built by Kumargupta I.
AHOM KINGDOM
Prime Minister made visit to Sivasagar’s Jerenga Pothar in Assam, which has historical significance related to Ahom Kingdom.
• Sivasagar (formerly known as Rangpur) was the seat of the powerful Ahom dynasty, who ruled Assam for six centuries (1228-1826).
• Jerenga Pothar in Sivasagar town is popularly connected to the valour of 17th century Ahom princess Joymoti(wife of the Ahom prince Gadapani).
• Ahoms migrated to the Brahmaputra valley from present-day Myanmar.
SAGARIKA
• It is India’s first full-fledged international cruise terminal being set up at Cochin Port in Kerala.
o Kochi has emerged as a major cruise destination in recent years.
• It will bring personnel of customs, Bureau of Immigration and CISF under one roof, thus speeding up paperwork.
BIODIVERSITY HERITAGE SITE
• Devalsari region in Tehri Garhwal district is likely to be declared as first biodiversity heritage site of Uttarakhand.
o The region is rich in biodiversity and has a lot of potential for ecotourism.
About Biodiversity Heritage Sites (BHS)
o BHS are areas that are unique, ecologically fragile ecosystems having rich biodiversity comprising of any one or more of the components such as;
✓ species richness,
✓ high endemism,
✓ presence of rare, endemic and threatened species, keystone species.
SOLAR OUTSHINES WIND POWER IN TOTAL CAPACITY
• As per Ministry of New and Renewable Energy data, total installed capacity of solar power stood at 38,794 MW, while total wind power capacity was 38,684 MW.
o In comparison, a decade ago, the solar segment had a capacity of 18 MW, while wind power’s installed capacity was 13,000 MW.
Key reasons for this:
o Supportive government policies, like National Solar Mission, Renewable Purchase Obligation, Pradhan Mantri KisanUrja Suraksha evam UtthanMahabhiyan Yojana etc.
o Land Certainty due to Solar Park Policy under which large tracts of land were identified.
o Lower solar tariffs dropping below grid electricity tariffs, leading to quicker adoption.
o Role of International Solar Alliance (ISA) to scale up of solar energy.
INTENSIFIED MISSION INDRADHANUSH
• Union Health Minister launched Intensified Mission Indradhanush 3.0.
About Intensified Mission Indradhanush:
• In 2014, Mission Indradhanush was launched to strengthen and re-energize the programme and achieve full immunization coverage for all children and pregnant women at a rapid pace.
Aim of IMI
o The focus of special drive was to improve immunisation coverage in select districts and cities to ensure full immunisation to more than 90% by December 2018.
o Enhance political, administrative and financial commitment through advocacy with key ministries/ departments and stakeholders towards full immunization coverage for each child.
o Reach all children with all UIP vaccines due for the age as per the national immunization schedule in the geographic area with focus on children up to 2 years of age and pregnant women. However, vaccination will be provided to children up to 5 years of age.
o Sustain the gains made through Intensified Mission Indradhanush through routine immunization by using IT based platforms for further planning and follow-up.
