POLITY AND GOVERNANCE
THE CONSUMER PROTECTION ACT, 2019
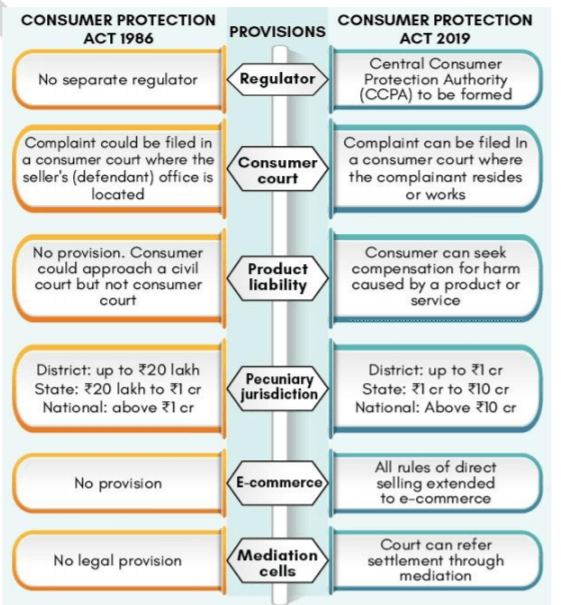
The Consumer Protection Act, 2019 replacing the earlier 1986 Act came into force.
Need for the new Act
The previous act i.e. the Consumer Protection Act, 1986 suffered from the following major shortcomings:
• Provided for a single point access to justice, which was time consuming.
• Did not cover e-commerce retailers/platforms under its ambit.
• Was not in sync with the new market dynamics, multi-layered delivery chains, and innovative and often misleading advertising and marketing machinery.
• No provision for the authority to take suo moto action against any person guilty of a violation under the Act or an unfair trade practice undermining the rights of a consumer.
• Penal steps could be taken only through a judicial process before the State or District Consumer Redressal Forums.
Major Provisions under the 2019 Act:
• Creation of Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA)
o Its primary objective is to promote, protect and enforce the rights of consumers and will be assisted by a Director General of Investigation which will look into cases and submit its report to the Authority.
• Simplification of consumer dispute adjudication process
o State and District Commissions are now empowered to review their own orders
o Empowerment of Consumer Commissions to enforce their orders.
o Deemed admissibility of complaints if the question of admissibility is not decided within the specified period of 21 days.
• Alternate Dispute Resolution mechanism
o A complaint will be referred by a Consumer Commission for mediation, wherever scope for early settlement exists and parties agree for it.
o Mediation will be held in the Mediation Cells to be established under the aegis of the Consumer Commissions.
o No appeal against settlement through mediation.
Six “consumer rights” provided in the new Act:
• the right to be protected against the marketing of goods, products or services which are hazardous to life and property.
• the right to be informed about the quality, quantity, potency, purity, standard and price of goods, products, or services to protect the consumer against unfair trade practices.
• the right to be assured, wherever possible, access to a variety of goods, products, or services at competitive prices.
• the right to be heard and to be assured that consumer’s interests will receive due consideration at appropriate fora.
• the right to seek redressal against unfair trade practice or restrictive trade practices or unscrupulous exploitation of consumers; and
• the right to consumer awareness.
INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
INDIA-E.U. RELATIONS
Recently, the 15th India- European Union (EU) Summit was held through a virtual medium.
Key Outcomes of the Summit
• ‘India-EU Strategic Partnership: A Roadmap to 2025’ was adopted to guide cooperation between India and the EU over the next five years.
• Agreed to establish regular High-Level Dialogue to guide negotiations on Broadbased Trade and Investment Agreement (BTIA) and to address multilateral issues of mutual interest.
• Agreement between India-EURATOM (European Atomic Energy Community) on research and development cooperation in the peaceful uses of nuclear energy was signed.
• Adopted declarations on Resource Efficiency and Circular Economy, decided to launch a dialogue on maritime security, renewed Agreement on Scientific cooperation.
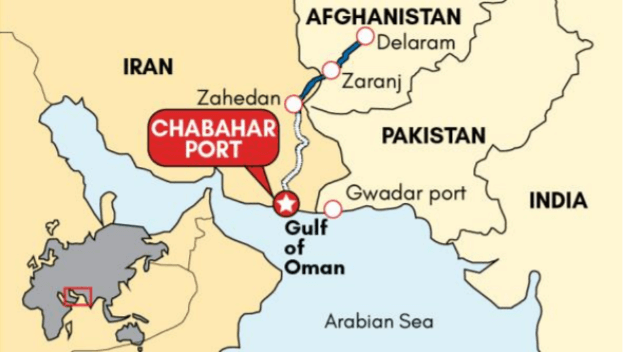
CHABAHAR – ZAHEDAN RAILWAY LINE
Iran has decided to proceed with the construction of rail line from Chabahar port to Zahedan, along the border with Afghanistan, without India.
Background
• In 2016, the Trilateral Agreement on Establishment of International Transport and Transit Corridor was signed among India, Iran and Afghanistan.
o The transit and transportation corridor allows Indian goods to reach Afghanistan through Iran, bypassing
Pakistani territory, and complements the Zaranj-Delaram highway built by India in Afghanistan in 2009.
• Under this agreement, India committed towards developing Chabahar port as well the land-based route connecting the port to Afghanistan.
• India also signed a pact with Iran to provide requisite services for the construction of Chabahar-Zahedan railway line, that cuts down travel time from the Chabahar port to the Iran-Afghanistan border
Reasons for exclusion of India from the project
• Delays due to U.S. sanctions: USA re-imposed sanctions on Iran after withdrawal from Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action. While India was given a special waiver for Chabahar port and rail line, the project suffered due too bureaucratic delays in USA for actual clearance of the import of heavy equipment.
o difficulties in finding equipment suppliers and funding partners due to worries they could be targeted by the U.S.
• Bureaucratic and diplomatic hurdles in India: such as operational hurdles, delays in dispersal of funds, lack of effective communication and diplomatic coordination etc.
o For instance, Iran is also going ahead with developing the Farzad-B gas block without India.
Rising Chinese influence in Iran
• Belt and Road Initiative (BRI): Under the BRI umbrella, China is presentlystrengthening its ties with Iran, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Egypt and other MiddleEast countries using engagements such as construction of stadiums, railways,industrial parks, 5G highways, clean energy project etc.
• Recently agreed 25-year comprehensive strategic cooperation between Iran-China: The draft 25-year, $400 billion agreement includes allocations in Iran’s transport, manufacturing sector and hydrocarbon industries which will give way to Chinese companies, equipment and workers in Iran.
• Gwadar-Chabahar connectivity: Iran proposed a tie-up between Gwadar and Chabahar last year. It can impinge on India’s strategic ties with Iran, restrict the use of Chabahar port for India and aggravate India’s security calculus in the immediate Western Indian Ocean.
• Bandar-e-Jask port: Iran has offered interests to China in this port located just 350km away from Chabahar. The Bandar-e-Jask port can extend China’s control along the Pakistan-Iran coast.
UNITED NATIONS CONVENTION ON THE LAW OF THE SEA (UNCLOS)
Recently, the Permanent Court of Arbitration (PCA) has given the ruling in Enrica Lexie case for killing of two Keralite fishermen.
• The Enrica Lexie case is an ongoing international controversy about a shooting off two Indian fishermen at the western coast of India in 2012 by two Italian Marines.
• In 2015, Italy had filed case against India for detaining its two marines and took the case to International Tribunal for the Law of the Sea (ITLOS) under United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS).
o ITLOS had later referred the matter to Permanent Court of Arbitration (PCA).
• India had claimed that the marines had violated the freedom of navigation rights under UNCLOS and should pay compensation.
o India held that the incident occurred within its contiguous zone, and comes under its jurisdiction.
• In this, now PCA has ruled that:
o India is entitled to claim compensation from Italy.
o However, India does not have jurisdiction to try the Italian marines, entitled to immunity as they were acting on behalf of a state.
o It further said that the Italian vessel had violated the right and freedom of navigation of the Indian fishing vessel under the UNCLOS.
o The award is final and without appeal, as India is a party to the UNCLOS.
Permanent Court of Arbitration (PCA)
• It was established by the Convention for the Pacific Settlement of International Disputes, concluded at The Hague in 1899.
• It is an intergovernmental organization providing a variety of dispute resolution services involving various combinations of states, state entities, international organizations and private parties.
• PCA has a three-part organizational structure consisting of:
o an Administrative Council that oversees its policies and budgets,
o a panel of independent potential arbitrators known as the Members of the Court,
o its Secretariat, known as the International Bureau, headed by the Secretary-General.
• It’s headquartered is situated in Hague, Netherlands.
• India is its member.
About UNCLOS
• It is an international agreement that resulted from the third United Nations Conference on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS III).
o It was adopted in 1982 and replaced the quad-treaty 1958 Convention on the High Seas and came into force in 1994.
• It is also called the Law of the Sea Convention or the Law of the Sea treaty.
• It defines the rights and responsibilities of nations with respect to their use of the world’s oceans, establishing guidelines for businesses, the environment, and the management of marine natural resources.
• Currently 167 countries and the European Union have joined in the Convention.
• India signed the Convention in 1982 and ratified in 1995.
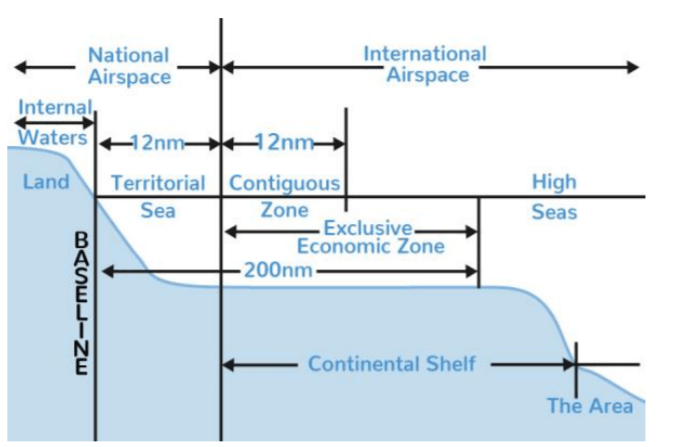
UNCLOS divides marine areas into FIVE main zones:
• There is the low-water line called Baseline along the coast as officially recognized by the coastal state.
• Internal Waters: These are waters on the landward side of the baseline from which the breadth of the territorial sea is measured.
o Each coastal state has full sovereignty over its internal waters as like its land territory. E.g. bays, ports, inlets, rivers and lakes that are connected to the sea
• Territorial Sea: It extends seaward up to 12 nautical miles (nm) from its baselines.
o The coastal states have sovereignty and jurisdiction over the territorial sea. These rights extend not only on the surface but also to the seabed, subsoil, and even airspace.
• Contiguous Zone: It extends seaward up to 24 nm from its baselines.
o It is an intermediary zone between the territorial sea and the high seas.
o The coastal state has the right to both prevent and punish infringement of fiscal, immigration, sanitary, and customs laws within its territory and territorial sea.
o Unlike the territorial sea, the contiguous zone only gives jurisdiction to a state on the ocean’s surface and floor. It does not provide air and space rights.
• Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ): Each coastal State may claim an EEZ beyond and adjacent to its territorial sea that extends seaward up to 200 nm from its baselines.
o Within EEZ, a coastal state has sovereign rights for the purpose of exploring, exploiting, conserving and managing natural resources, whether living or non-living, of the seabed and subsoil.
o Rights to carry out activities like the production of energy from the water, currents and wind.
o Unlike the territorial sea and the contiguous zone, the EEZ only allows for the above-mentioned resource rights. It does not give a coastal state the right to prohibit or limit freedom of navigation or overflight, subject to very limited exceptions.
• High Seas: The ocean surface and the water column beyond the EEZ are referred to as the high seas.
o It is beyond any national jurisdiction. States can conduct activities in these areas as long as they are for peaceful purposes, such as transit, marine science, and undersea exploration.
ECONOMY
PRIVATE PARTICIPATION IN RAILWAYS
Ministry of Railways has invited private participation for operation of passenger train services over 109 Origin Destination (OD) pairs of routes using 151 modern trains on existing rail infrastructure.
• Indian Railways (IR) is the largest passenger and fourth largest freight transporting railway system globally.
• Bibek Debroy Committee in 2015 recommended that private entry into running both freight and passenger trains should be allowed.
• Consequently, Indian Railway Catering and Tourism Corporation Limited (IRCTC), in which the government is the majority shareholder, was given pilot Tejas operations which were the first trains allowed to be run by a ‘non-Railway’ operator.
About the recent step
• It would be the first initiative of private investment for running passenger trains over Indian Railways network attracting investments of an estimated ₹30,000 crore which is expected to begin in 2023.
• Objectives:
o to introduce modern technology rolling stock with reduced maintenance,
o reduced transit time, boost job creation, provide enhanced safety,
o provide world class travel experience to passengers,
o reduce demand supply deficit in the passenger transportation sector.
• Responsibility of Private Entity:
o It shall be responsible for financing, procuring, operation and maintenance of the trains.
o The operation of the trains by the private entity shall conform to the key performance indicators like punctuality, reliability, upkeep of trains etc.
o Private firms will have the freedom to decide fares and stoppages, and also the basket of services on offer in these trains.
• Responsibility of IR:
o The driver and guard of the trains will Railway officials who will operate these trains, maintain track infrastructure etc.
PUBLIC-PRIVATE PARTNERSHIP
Types of investment models
• Build Operate and Transfer (BOT) Toll model:
o Under this model, a road developer constructs the road and he is allowed to recover his investment through toll collection.
o There is no government payment to the developer as he earns his money invested from tolls.
• BOT Annuity Model:
o A developer builds a highway, operates it for a specified duration and transfers it back to the government.
o The government starts payment to the developer after the launch of commercial operation of the project.
• Engineering, Procurement and Construction (EPC) Model:
o Under this model, the cost is completely borne by the government. Government invites bids for engineering knowledge from the private players.
o Procurement of raw material and construction costs are met by the government.
o The private sector’s participation is minimum and is limited to the provision of engineering expertise
• Hybrid Annuity Model (HAM)
o HAM is a mix of BOT Annuity and EPC models.
o As per the design, the government will contribute to 40% of the project cost in the first five years through annual payments (annuity).
o The remaining payment will be made on the basis of the assets created and the performance of the developer.
SECURITY
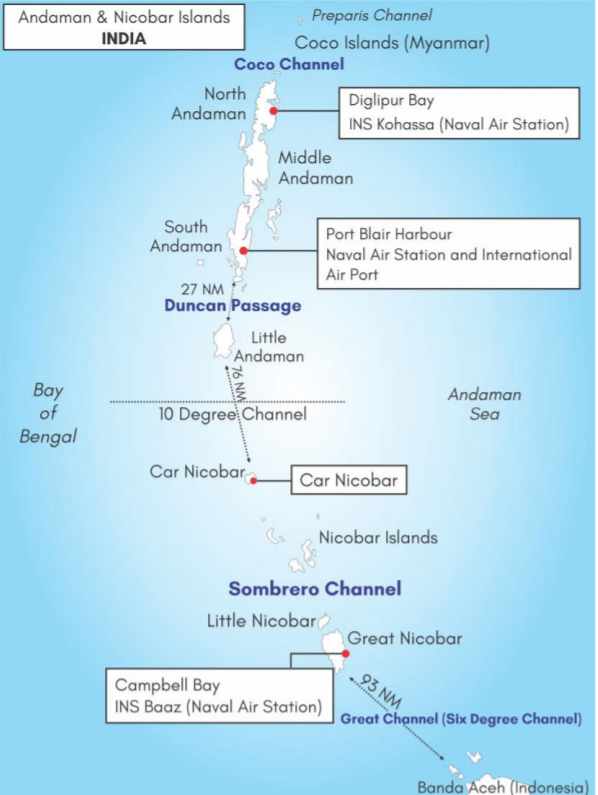
MILITARIZATION OF ANDAMAN AND NICOBAR ISLANDS
The Ladakh stand-off with China has catalysed India’s efforts to strengthen its military presence at the Andaman and Nicobar Islands (ANI).
• Government plans for basing additional military forces, including facilities for additional warships, aircraft, missile batteries and infantry soldiers at the strategically located Andaman Islands.
• Runways at Naval air stations INS Kohassa in Shibpur and INS Baaz in Campbell Bay are being extended to support operations by large aircraft.
• Indian strategic commentators are even recommending to permit friendly foreign navies access to the ANI’s military bases.
About Andaman & Nicobar Islands group
• It is a group of 572 islands, out of which only 38 are inhabited.
• The islands extend from 6° to 14° North latitudes and from 92° to 94° East longitudes.
• The highest point is Saddle Peak (732 m) located in North Andaman Island.
• The only active volcano in India, Barren Island, is located in A&N and had last erupted in 2017.
• It also has mud volcanoes have erupted mud volcano situated in Baratang island sporadically
• It has often been referred to as India’s ‘unsinkable aircraft carrier’ to the East.
AGRICULTURAL EMISSIONS IN INDIA
Recently Union Government launched Green-Ag Project to reduce emissions from agriculture.
About Green-Ag Project
• It aims to bring at least 104,070 ha of farms under sustainable land and water management and ensure 49 million Carbon dioxides equivalent sequestered or reduced through sustainable land use and agricultural practices.
• Project will be implemented in Mizoram, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha and Uttarakhand.
• It is funded by the Global Environment Facility (GEF)
o Global Environment Facility (GEF) established on the eve of the 1992 Rio Earth Summit.
o The World Bank serves as the GEF Trustee, administering the Fund.
Agricultural emissions in India
• In India agriculture and livestock accounts for 18% of gross national emissions, the third-highest sector after energy and industry.
o Out of this more than 85% of emissions are due to cattle production system, rice cultivation and ruminant meat and remaining 15% comes from other crops and nitrous oxide emitted from fertilizers.
• Most of the GHG emission from Indian agriculture takes places from states like Punjab, Haryana, UP, Bihar, West Bengal etc.
VIRTUAL WATER
Experts are suggesting virtual water trade as one of the alternatives to ensure sustainable water consumption.
What is Virtual Water Trade?
• Virtual water (VW) is the water ‘embodied’ in a product, not in real sense, but in virtual sense. It refers to the water needed to produce a product.
• Virtual water trade (VWT) refers to the import and export of hidden water in the form of products such as crop products, textiles, machinery and livestock — all of which require water for their production.
• According to the Water Footprint Network (WFN) database, India had the lowest virtual imports of water in the world.
o India is a net virtual water exporter because of agricultural products.
o Rice was the highest exported food product, followed by buffalo meat and maize.
• As a result, the amount of water taken out of Indian rivers is way more than that goes back in through natural rainfall and melting snow.
• Inter-state VWT, especially of food grains, has revealed an unsustainable pattern of water usage in certain parts of India.
• Punjab and Haryana, despite being among the most water stressed regions in the country, have been the source of a majority of water intensive food grains trade to water stressed states like Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu.
HYDROPOWER PROJECTS IN NORTHEAST
The Forest Advisory Committee (FAC) has recently deferred its decision on the controversial Etalin Hydropower project located in Arunachal Pradesh.
• 3097 MW Etalin Hydropower Project is proposed to be constructed over Dri and Tangon Rivers, situated inside the Dibang catchment zone in Arunachal Pradesh.
• The project has been awaiting forest clearance since 2014 and close to 3 lakh trees are expected to be felled to make way for the dam.
• Dibang valley falls in one of India’s most active seismic zones.
Major upcoming Hydro Electric (H.E.) plants in N.E. India
• Mizoram: Tuirial H.E. Project on Tuirial river
• Nagaland: Doyang H.E. Project on river Doyang (a tributary of the River Brahmaputra)
• Assam: Kopili H.E. Project on Kopili River
• Arunachal Pradesh:
o Ranganadi H.E. Project on Ranganadi river
o Pare H.E. Project on river Dikrong (tributary of river Brahmaputra)
o Kameng H.E. Project utilizes the flows from Bichom and Tenga Rivers (both tributaries of the River Kameng).
TIGER STATUS REPORT 2018
Fourth tiger census report, Status of Tigers, Co-predators, Prey and their Habitat, 2018 shows the count of tigers in India, has risen to 2967, in 2018 from 2,226 in 2014.
• Report assesses the status of tigers in terms of spatial occupancy and density of individual populations across India.
• Technologies used in this assessment:
o M-STrIPES (Monitoring system for tigers – intensive protection and ecological status) using GPS to geotag photo-evidences and survey information, made this exercise more accurate
o CaTRAT (Camera Trap data Repository and Analysis Tool) for automated segregation of camera trap photographs to species.
o India already achieved the target of doubling the count.
• At 2,967, India hosts 70% of the world’s tigers. Tigers were observed to be increasing at a rate of 6% per annum (2006 to 2018). Nearly a third of India’s tigers are living outside tiger reserves.
• Madhya Pradesh (526) has the maximum number of tigers followed by Karnataka (524) and Uttarakhand (442).
• Largest contiguous tiger population in the world of about 724 tigers was found in the Western Ghats (Nagarhole-Bandipur Wayanad -Mudumalai- Satyamangalam BRT block).
SOCIAL ISSUES
NEW EDUCATION POLICY 2020
• Union Cabinet has approved the New Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
• The Cabinet has also approved the renaming of the Ministry of Human Resource Development to the Ministry of Education.
• The NEP cleared by the Cabinet is only the third major revamp of the framework of education in India since independence. The two earlier education policies were brought in 1968 and 1986.
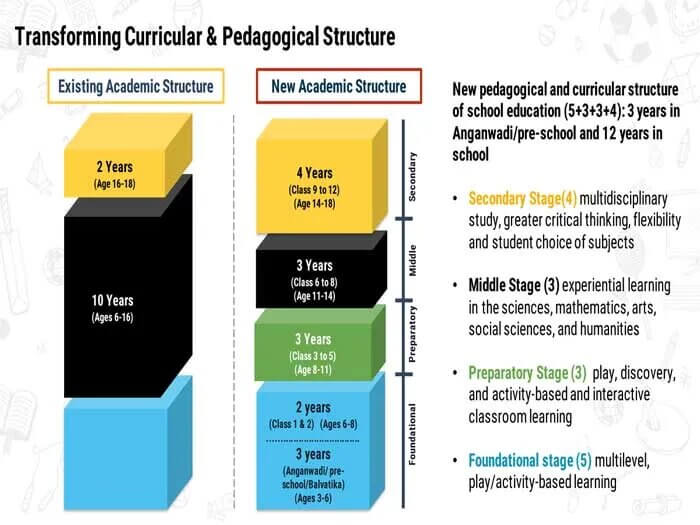

Education in India
Constitutional Provisions:
• Part IV of Indian Constitution, Article 45 and Article 39 (f) of Directive Principles of State Policy (DPSP), has a provision for state-funded as well as equitable and accessible education.
• The 42nd Amendment to the Constitution in 1976 moved education from the State to the Concurrent List.
• The education policies by the Central government provide a broad direction and state governments are expected to follow it. But it is not mandatory, for instance Tamil Nadu does not follow the three-language formula prescribed by the first education policy in 1968.
• The 86th Amendment in 2002 made education an enforceable right under Article 21A.
Related Laws:
• Right to Education (RTE) Act, 2009 aims to provide primary education to all children aged 6 to 14 years and enforces education as a Fundamental Right.
• It also mandates 25% reservation for disadvantaged sections of the society where disadvantaged groups
Government Initiatives:
• Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan, Mid Day Meal Scheme, Navodaya Vidyalayas (NVS schools), Kendriya Vidyalayas (KV schools) and use of IT in education are a result of the NEP of 1986.
CULTURE
GURJARA-PRATIHARAS
Natesa, a 9th century’s rare sandstone idol of Rajasthan temple smuggled out of country in 1998 returned to India.
About Natesa sandstone idol
• Natesa is a rare sandstone idol from the Pratihara Style of architecture in Rajasthan.
• It is originally from the Ghateswar Temple at Baroli, Rajasthan.
• The sandstone Natesa figure stands tall at almost 4 ft in a rare and brilliant depiction of Shiva.
o A depiction of Nandi (sacred bull calf) is shown behind the right leg of the Natesa icon.
• Pratihara Style of architecture is associated with Gurjara-Pratihara dynasty around 800-900 AD.
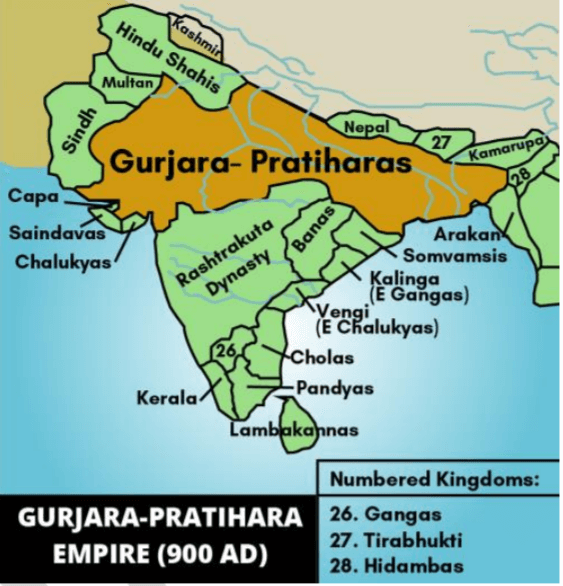
o Gurjara-Pratihara dynasty ruled much of Northern India from the mid-8th to the 11th century.
o They were one of the first four patrilineal clans of the caste group referred to as the Rajputs.
o The Pratiharas, derived their name from the Sanskrit meaning doorkeeper, are seen as a tribal group or a clan of the Gurjaras.
o Important rulers:
▪ Nagabhata I contained Arab armies moving east of the Indus River and rose to fame in the late 8th century CE.
▪ Nagabhata Il, Mhir Bhoj (Bhoja) and Mahendrapala I were the other important rulers of dynasty.
o The expansion of the Gurjara-Pratihara kingdom involved constant conflicts with other contemporary powers such as the Palas and the Rashtrakutas known as the tripartite struggle.
MISCELLANEOUS
OPERATION SAMUDRA SETU
• Indian Navy has completed Operation Samudra Setu which was aimed at bringing nearly 4,000 Indian citizens from overseas during the COVID-19 pandemic.
• Indian Naval Ships Jalashwa, Airavat, Shardul and Magar participated in the operation.
• Earlier evacuation operations by Indian navy: Operation Sukoon in 2006 (Beirut) and Operation Rahat in 2015 (Yemen).
FISH CRYOBANKS
• Ministry for Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying has announced setting up of fish cryobanks. This would be the first time in the world when “Fish Cryobank” will be established.
• It will facilitate all time availability of fish sperms of desired species to fish farmers.
PROTECTED AREAS – DEHING PATKAI
Assam Government has decided to upgrade the Dehing Patkai Wildlife Sanctuary to a National Park.
• Dehing Patkai Wildlife Sanctuary is referred as ‘The Amazon of East’.
o Dehing is the name of the river that flows through this forest and Patkai is the hill at the foot of which the sanctuary lies
• It is the only rainforest in Assam which spreads across Tinsukia, Dibrugarh and Sivasagar districts of Assam and also stretches till the State of Arunachal Pradesh.
KAZI 106F
• It is India’s only Golden Tiger found in Kaziranga National Park of Assam.
• A golden tiger, also called tabby tiger or strawberry tiger, is a tiger with a color variation caused by a recessive gene.
o The yellow skin of tigers is controlled by a set of ‘agouti genes’ while the black stripes are controlled by ‘tabby genes’ and their alleles. Suppression of any of these genes may lead to color variation in a tiger.
HIMACHAL PRADESH: FIRST STATE WITH 100% LPG CONNECTIONS
• Himachal Pradesh has become the first state in the country where 100 per cent households have LPG connections.
• Earlier, state launched Himachal Grihini Suvidha Yojana to cover the families left-out under Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY).
• PMUY is a scheme of the Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas for providing free LPG connections to women from Below Poverty Line (BPL) households.
BELYO
• It is country’s first COVID-19 blockchain platform.
• It will convert COVID-19-related clinical and vaccination data of citizens currently from the physical form into digital assets.
• This data then can be retrieved by contact tracing apps like Aarogya Setu.
WINTER DIESEL
• Winter diesel is a specialised fuel that was introduced by Indian Oil Corporation specifically for high altitude regions and low-temperature regions such as Ladakh, where ordinary diesel can become unusable.
Benefits of winter diesel
o Contains additives to maintain lower viscosity can be used in temperatures as low as -30°C
o Higher cetane rating-an indicator is the combustion speed of diesel and compression needed for ignition.
o Lower sulphur content, which would lead to lower deposits in engines and better performance.
SIDDI COMMUNITY
• Siddi community has got its first representative in Karnataka State legislature.
• They are an ethnic group inhabiting India and Pakistan.
• They are descendants of Africans from North-East and East Africa who were brought to India as slaves, soldiers or servants.
• In India, they are spread along the coast of Gujarat, Karnataka, Maharashtra and Andhra Pradesh.
• Current estimated population: 20,000–55,000 individuals.
KASHMIR SAFFRON GETS GEOGRAPHICAL INDICATION (GI) CERTIFICATE
• Kashmir saffron is the only saffron in the world that is grown at an altitude of 1,600 meters.
• It has unique characteristics like longer and thicket stigma, natural deep-red colour, high aroma etc.
HAGIA SOPHIA, TURKEY
• Recently, Hagia Sophia, an iconic Istanbul museum has been converted into mosque.
• It was originally built as the cathedral for the capital of the Eastern Roman Empire in the sixth century, and became a mosque in 1453 with the Ottoman conquest of Constantinople.
• In 1934 it became a museum and is now a UNESCO World Heritage site.
INDIGENOUS MANGO HERITAGE AREA
• Recently, Kannapuram Panchayat in Kannur town in Kerala has been declared as Indigenous Mango Heritage Area.
• Kannapuram is home to over 200 varieties of mangoes, and is home to various indigenous mango varieties.
MAHALANOBIS AWARD
• The first Prof. P. C. Mahalanobis National Award in Official Statistics for lifetime achievement was conferred on Dr. C. Rangarajan in recognition of his outstanding contribution in laying the foundation for holistic reforms in national statistical system.
o Dr. C. Rangarajan is former Chairman, National Statistical Commission and former RBI Governor.
• Prof. P. C. Mahalanobis National Award was instituted by Ministry of Statistics & Programme Implementation in 2019 for recognizing outstanding achievement of official statisticians in Central Government, State Governments and Institutions.
