DU LLM 2021 Question Paper
Looking for DU LLM Online Coaching?
You have come to the right place! We offer comprehensive online and postal study material for the LLM entrance exams.
Click Here to Know More- Under section 423 of the companies Act, 2013 any person who is aggrieved by an order of the National Company Law Appellate Tribunal may approach the supreme court on any question of law within___ days from the date of receipt of the order of the Appellate to him on any question of law arising out of such order.
(a) 30 days
(b) 45 days
(c) 60 days
(d) 90 days
- What is the maximum number of directors a one person company can have under companies act, 2013?
(a) 1
(b) 3
(c) 15
(d) 17
- A company licensed under section 8 of the companies act, 2013 may alter the provisions contained in its memorandum or articles only after obtaining the previous approval of __
(a) The central government
(b) The tribunal
(c) The court
(d) The state government
- Under the companies act, 2013, the paid up capital and turnover of a small company shall not exceed rupees___ and rupees__ respectively
(a) 50 lakhs, 10 crores
(b) 2 crores, 20 crores
(c) 2 crores, 10 crores
(d) 50 lakhs, 2 crores
- Under which doctrine, outsiders dealing with the company are entitled to assume that as far as internal proceedings of the company are concerned, everything has been done regularly?
(a) Ultra vires
(b) Constructive notice
(c) Indoor management
(d) Alter ego
- What is the legal status of a promoter in relation to a company?
(a) An agent
(b) A trustee
(c) Both an agent and a trustee
(d) Neither an agent nor a trustee
- First annual general meeting of a newly incorporated company which is registered under the provisions of the companies act, 2013 is to be held within___
(a) 6 months from the date of closing of the first financial year
(b) 9 months from the date of closing of the first financial year
(c) 6 months from the date of closing the first calendar year
(d) 9 months from the date of closing the first calendar year
- Identify the correct statement or statements on high court in India from the following:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
(a) A, B and C
(b) A only
(c) B only
(d) C only
- Government of NCT of Delhi v. Union of India, 2018(8) SCC 502, is a decision of the constitution bench of the supreme court on the interpretation of Article ____ of the constitution.
(a) 368
(b) 301
(c) 243-A
(d) 239-AA
- Which one of the following is not a decision on the power of parliament to amend the constitution of India and procedure therefore?
(a) Golak Nath v. State of Punjab
(b) Kesvananda Bharti v. State of Kerala
(c) Union of India v. Naveen Jindal
(d) Minerva Mills Ltd. V. Union of India
- Which of the following is correct?
(a) Part VIII of the constitution deals with co-operative societies
(b) Part IX-A of the constitution of India deals with Municipalities
(c) Part IX-B of the constitution of India deals with Panchayats
(d) Part X of the constitution of India deals with Languages
- Math List I with List II
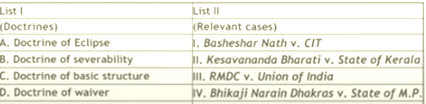
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-I, B-II, C-III, D-IV
(b) A-IV, B-III, C-II, D-I
(c) A-II, B-I, C-IV, D-III
(d) A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II
- In which of the following cases the Supreme court of India held that the freedom of speech and expression thorough the medium of integral part of Article 19(1)(a) of the constitution of India?
(a) Indian Express v. Union of India
(b) Shreya Singhal v. Union of India
(c) Anuradha Bhasin v. Union of India
(d) CPIO v. Subhash Chandra Aggarwal
- Which of the following is a decision on the meaning of ‘State’ as defined under Article 12 of the Constitution of India?
(a) Keshavan Madhava Menon v. State of Bombay
(b) Basheshar Nath v. CIT
(c) Charanjit Lal Choudhary v. Union of India
(d) Pradeep Kumar Biswas v. India Institute of Chemical Biology
- In which case the supreme court of India held the following?”we think that the right to life includes the right to live with human dignity and all that goes along with it, namely, the bare necessaries of life such as adequate nutrition, clothing and shelter and facilities for reading, writing and expressing oneself in diverse forms, freely moving about and mixing and commingling with fellow human beings.”
(a) K. Gopalan v. State of Madras
(b) Nandini Sunder v. State of Chhattisgarh
(c) Consumer Education and Research Center v. Union of India
(d) Francis Coratle Mullin v. UT of Delhi
- Which among the following cases led to adding of clause(4) to article of the constitution of India by the constitution (1st Amendment) Act, 1951?
(a) R. Balaji v. State of Mysore
(b) Rajendran v. State of Madras
(c) State of Madras v. Champakam Dorairajan
(d) State of Uttar Pradesh v. Pradip Tandon
- Identify the correct statement or statements on the jurisdiction of the supreme court of India from the following?
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and C
(b) A and B only
(c) A only
(d) C only
- Which of the following statement is correct in the context of the Indian Contract Act, 1872?
(a) Stranger to contract can enforce a promise
(b) Stranger to consideration can enforce a promise
(c) Stranger to consideration is stranger to contract
(d) Stranger to consideration cannot enforce a promise
- As per section 16 of the Indian contract act, 1872, a person is deemed to be in a position to dominate the will of another where:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A and B only
(b) A, B and D only
(c) A, B and C only
(d) A, B, C and D
- A promises to obtain for B an employment in the public service and B promises to pay 1000 rupees to A. The agreement is___
(a) Void
(b) Voidable
(c) Valid
(d) Enforceable
- Which of the following cases is related to the principle that acceptance, in the context, must be communicated to the offer or himself?
(a) Belfour v. Balfour
(b) Harvey v Facey
(c) Felthouse v Bindley
(d) Lalman Shula v Gauri Datt
- B accepts A’s proposal by posting a letter of acceptance to A. The above acceptance__
(a) Cannot be revoked by B
(b) Can be revoked by B at any time before the letter of acceptance reaches A
(c) Can be revoked by B at any time before or at the movement when the letter of acceptance reaches A.
(d) Can be revoked by B at any time after the letter or acceptance reaches A
- Who among the following may dispense with or remit performance of promise under section 63 of the Indian Contract Act, 1872?
(a) Promisee
(b) Promisor
(c) Promise or promisor
(d) Any person
- A contract is not discharged by___
(a) Performance
(b) Breach
(c) Commercial hardship
(d) Novation
- X places an order with Y for supply of 50 radio sets. Y knows nothing of X’s mode of conducting his business. Y could not supply them in time. X loses a profitable contract due to non-receipt of the radio sets and claimed his loss of profit from Y. X will fail in his claim because the natural of loss is___
(a) Ordinary
(b) Remote
(c) Special
(d) Indirect
To access the remaining portion of the Paper, as well as Solutions and Answer Key,
Check out our Past Paper’s Packages
Click here for Past Papers’ PackagesLooking for DU LLM Online Coaching?
You have come to the right place! We offer comprehensive online and postal study material for the LLM entrance exams.
Click Here to Know More