POLITY
ONE NATION, ONE RATION CARD
- As part of the Economic relief package amid COVID 19 outbreak, the Central government has announced the national rollout of a ‘One Nation, One Ration Card’ system in all states and Union Territories by March 2021.
About One Nation, One Ration Card Scheme
- Under this ‘One Nation, One Ration Card’ system, beneficiary will be able to buy subsidized food grains from any FPS across Country using their existing/same ration card that is Aadhaar linked.
- Under present Public Distribution System (PDS), a ration cardholder can buy food grains only from Fair Price Shop (FPS) that has been assigned in the locality in which he/she lives.
- Once 100 per cent of Aadhaar seeding and 100 per cent installation of e-PoS devices is achieved, national portability of ration cards will become a reality. Currently, it is enabled in 17 States and UTs.
About Ration Card
- It is a document issued under an order or authority of State Government, as per PDS, for purchase of essential commodities from FPS at subsidized rates.
- State Governments issue distinctive Ration Cards to APL, BPL and Antyodaya families and conduct periodical review and checking of Ration Cards.
- Proof of identification: It has become an important tool of identification when applying for other documents like Domicile Certificate, for inclusion in Electoral Rolls, etc
National Food Security Act 2013 (NFSA)
- This marks a shift in approach to food security from welfare approach to rights-based approach.
- Act legally entitles up to 75% of the rural population and 50% of the urban population to receive subsidized foodgrains under Targeted Public Distribution System (TPDS).
- Under NFSA, about 81 crore persons are entitled to buy subsidized food grain, rice at Rs 3/kg, wheat at Rs 2/kg, and coarse grains at Re 1/kg — from their designated FPS of TPDS.
- It is operated under joint responsibility of Central and State Governments.
o Central Government- responsible for allocation of food grains to States/UTs, transportation of food grains up to designated depots and providing central assistance to States/UTs for delivery of food grains from FCI godowns to doorstep of FPSs.
o State Governments- handle operational responsibility including identification of eligible families and issue of Ration Cards and supervision of the functioning of Fair Price Shops (FPSs) etc. Targeted Public distribution system
- It was launched in 1997 to focus on poor. Under TPDS, beneficiaries are divided into 2 categories
o Below Poverty Line-BPL Households
o Above Poverty line- APL Households
- Antyodaya Anna Yojana was launched in 2000 to make TPDS more focused and targeted.
o It focuses poorest of the poor families among BPL beneficiaries.
INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
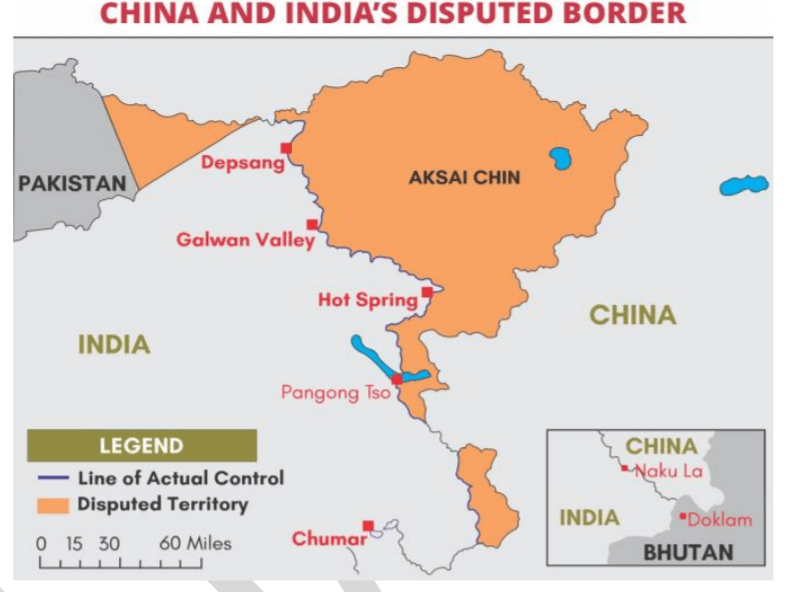
INDIA- CHINA BORDER DISPUTE
- The border tensions between China and India come to the forefront once again following the ongoing standoff between India and China in the North Sikkim and Ladakh region across the Line of Actual Control (LAC).
- The border between India and China is not clearly demarcated throughout and there is no mutually agreed Line of Actual Control (LAC).
- The LAC is the demarcation that separates Indian-controlled territory from Chinese-controlled territory. India considers the LAC to be 3,488 km long, while the Chinese consider it to be only around 2,000 km.
- The LAC is divided into three sectors, viz. Western, Middle and Eastern.
o The boundary dispute in the Western Sector (Ladakh) pertains to the Johnson Line proposed by the British in the 1860s that extended up to the Kunlun Mountains and put Aksai Chin in the then princely state of Jammu and Kashmir.
✓ India used the Johnson Line and claimed Aksai Chin as its own. China, however, do not recognise it and instead accepts McDonald Line which puts Aksai Chin under its control.
o In the Middle Sector (Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand), the dispute is a minor one. Here LAC is the least controversial except for the precise alignment to be followed in the Barahoti plains. India and China have exchanged maps on which they broadly agree.
o The disputed boundary in the Eastern Sector (Arunachal Pradesh and Sikkim) is over the McMahon Line (in Arunachal Pradesh) decided in 1914 in a meeting of Representatives of China, India, and Tibet in Shimla.
INDIA -TAIWAN
- Two Indian MPs, for the first time virtually attended the swearing-in ceremony of newly elected President of Taiwan.
India -Taiwan relations
o Post-independence, bilateral ties between India and Taiwan ceased to exist when in 1950 India accorded diplomatic recognition to People’s Republic of China (PRC).
o Further, during Cold War, even informal ties between New Delhi and Taiwan remained remote, as Taiwan joined the US-led block and India the nonaligned movement.
o This changed in the 1990s when Indian Government reoriented India’s policy towards Taiwan in the face of India’s domestic economic crises and foreign policy challenges.
o India and Taiwan set up unofficial relations in 1995 with establishment of the IndiaTaipei Association (ITA) in Taipei (Capital of Taiwan).
About Taiwan and One China Policy
- Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC) was formed in 1949.
- In 1949 Chinese Communist Party armies defeated Nationalist forces (Kuomintang party) and established People’s Republic of China (Present China).
- Nationalist forces fled to Taiwan resulting in the separation of Taiwan from China in 1949 and formation of ROC. Both sides said they represented all of China.
- Initially, many governments including US recognised Taiwan separately. But with shift of diplomatic relation the US held One China policy.
- According to One China Policy any country wishing to establish diplomatic relations with China (PRC) must acknowledge there is only ‘One China’ and sever all formal ties with Taiwan.
- Taiwan is not a member of the United Nations and WHO. But is member of WTO by name Chinese Taipei (Taiwan).
- 179 of the 193 member states of UN do not maintain diplomatic ties with Taiwan.
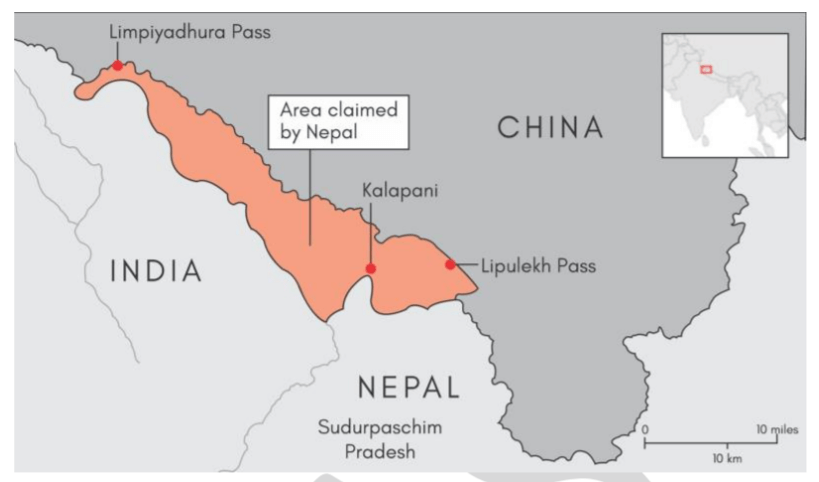
INDO-NEPAL TERRITORIAL DISPUTE
- Recently, Nepal unveiled a new political map that claimed strategically important land Kalapani, Limpiyadhura and Lipulekh of Uttarakhand as part of its sovereign territory.
- The map is in retaliation of Nepal’s objection to construction of road by India from Dharchula to Lipulekh in Uttarakhand.
o This road connects close to the Line of Actual Control and opens a new route for Kailash Mansarovar yatra via Lipulekh pass.
o This will help pilgrims to avoid dangerous high-altitude routes through Sikkim and Nepal.
- India termed recent action by Nepal as a `unilateral act’ which is not based on historical facts and evidence and also stated that these areas have always been part of the Indian Territory.
- Also, after the reorganisation of Jammu and Kashmir, India had published a new map in November 2019, which showed the region of Kalapani as part of the Indian territory.
- The new map—and the consequent objection from Nepal—brought forth the unresolved border disputes between the two countries.
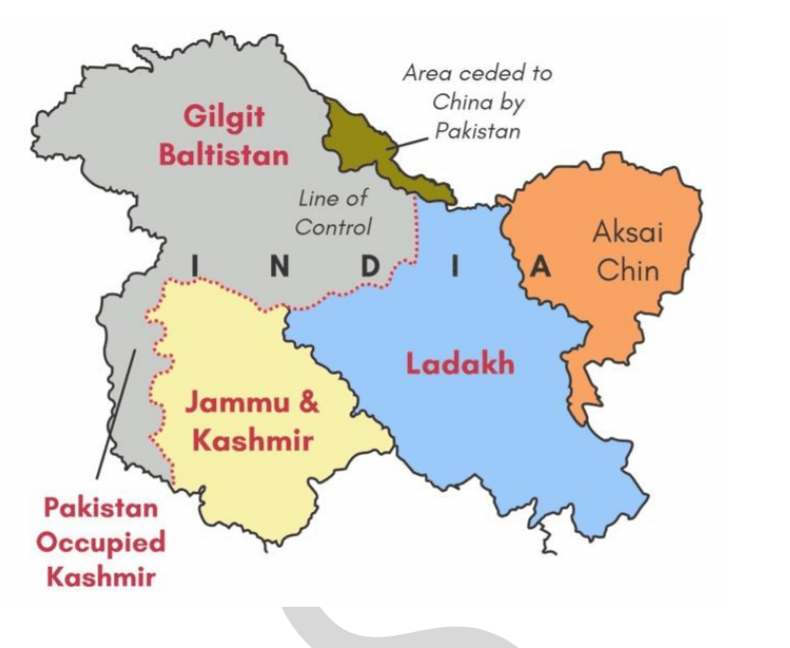
GILGIT BALTISTAN ISSUE
India lodged a strong protest against Supreme Court of Pakistan order on the Gilgit-Baltistan region.
- Pakistan’s Supreme Court has approved Federal government’s plea to amend Government of Gilgit-Baltistan Order, 2018.
- This allows Federal government to set up a caretaker government and conduct provincial Assembly elections in Gilgit-Baltistan region.
- said that entire Union Territories of Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh, including areas of Gilgit and Baltistan, are “integral part of India”.
About Gilgit Baltistan (GB) region
- The region was a part of erstwhile princely state of Jammu and Kashmir.
- It has been under Pakistan’s control since November 4, 1947, following invasion of Kashmir by tribal militias and Pakistan army.
- It was renamed as ‘Northern Areas of Pakistan’ and put under direct control of Pakistan federal government through Karachi Agreement, 1949.
NON-ALIGNED MOVEMENT
Indian Prime Minister participated in online Summit of Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) Contact Group 2020 to declare solidarity during COVID-19 Pandemic.
- Themed ‘United against COVID-19’ the Summit was aimed to promote international solidarity in the fight against the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Host - President of the Republic of Azerbaijan, current Chairman of NAM grouping.
About Non-Aligned Movement
- The Non-Aligned Movement was formed during the Cold War as an organization of States that did not formally align themselves with either the United States or the Soviet Union, but sought to remain independent or neutral.
- Origin: Asia-Africa Conference held in Bandung, Indonesia in 1955.
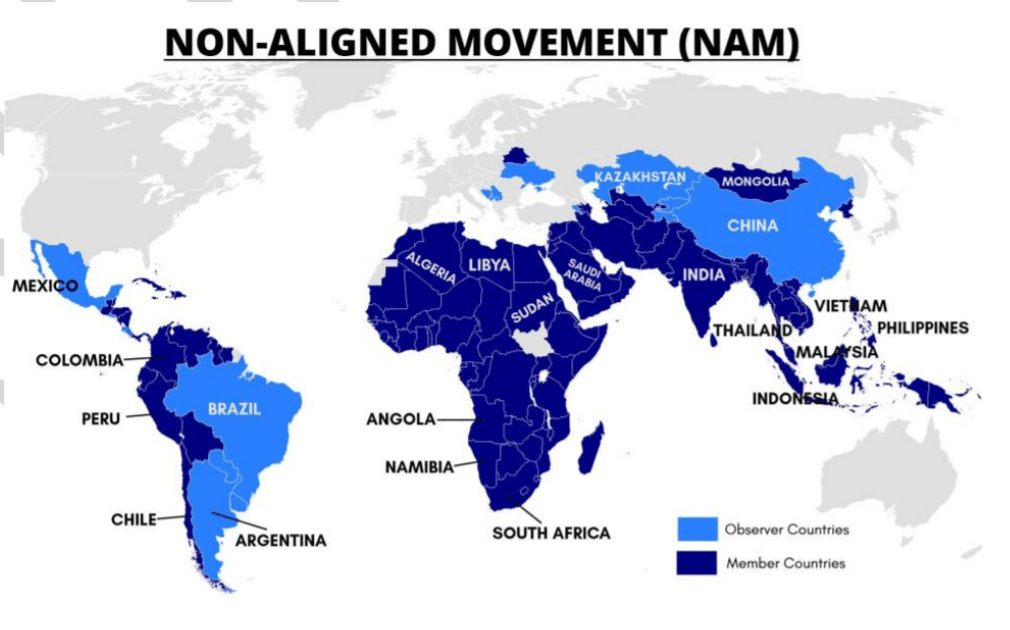
NAM’s first conference - The Belgrade Conference held in 1961 under the leadership of India, Yugoslavia, Egypt, Ghana, and Indonesia.
- It has 120 members comprising 53 countries from Africa, 39 from Asia, 26 from Latin America and the Caribbean and 2 from Europe (Belarus, Azerbaijan).
- Key principles of NAM: The policy of non-alignment was based on the five principles of Panchsheel. These principles were
o Mutual respect for each other’s territorial integrity and sovereignty
o Non-interference in each other’s military and internal affairs
o Mutual non-aggression
o Equality and mutual benefit
o Peaceful coexistence and economic cooperation.
NEW SECURITY LAW IN HONG KONG
Recently China’s National People's Congress (NPC) approved Hong Kong National Security Law.
- The law seeks to criminalise secession, subversion, terrorism and foreign interference in Hong Kong.
- It also says that China could have its own law enforcement agencies in Hong Kong, alongside the city's own to safeguard national security in accordance with the law.
- It raised concerns that, it could lead to prosecution of Hong Kongers for criticising their or the mainland's leadership, joining protests or exercising their current rights under local laws.
- Also, it is said to weaken “one country, two systems" under which China agreed to protect Hong Kong's extensive freedoms, autonomy and its independent legal system.
ECONOMY
ATMANIRBHAR BHARAT
The Prime Minister has announced Rs. 20 lakh crore stimulus and to ensure that all facets of the economy are addressed, 4L - Land, Labour, Liquidity and Laws all have been emphasized in this package.
- The idea of Atmanirbhar Bharat if based on 5 pillars:
o First Pillar is Economy, emphasizing on Quantum Jump rather than Incremental change.
o Second Pillar is Infrastructure.
o Third Pillar is Our System, a special reference has been made to technology and contemporary policies as part of this system.
o Fourth Pillar is Our Demography.
o Fifth pillar is Our Demand.
- The package has tried to address all sectors of the economy in different parts viz.:
o Part 1: Businesses including MSMEs.
o Part 2: Poor including migrants and Farmers.
o Part 3: Agriculture.
O Part 4: New Horizons of Growth.
o Part 5: Government Reforms and Enablers.
SARFAESI ACT
- A five-judge Constitution Bench of the Supreme Court (SC) recently held that cooperative banks can use the Securitisation and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest Act (SARFAESI Act) for recovery of debts from its defaulters and can seize and sell their assets to recover dues.
About SARFAESI Act, 2002
- The act was framed in order to address the problem of Non-Performing Assets (NPAs) or bad assets of banks/financial institutions through different mechanisms.
- It allows only secured creditors (lenders whose loans are backed by a security such as mortgage) to take possession over a collateral security if the debtor defaults in repayment.
ENVIRONMENT
LOCUST ATTACK
- Recently, Swarms of desert locusts invaded vast swathes of land in various Indian states which entered via Pakistan’s Sindh province
- Union government issued a warning to 12 states including Rajasthan, Punjab, Haryana and Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat and Maharashtra regarding the locust attack.
- The current attack is said to be the worst desert locust attack in 26 years.
Desert Locusts
- They belong to the family of grasshoppers and have life span of 90 days.
- Four species of locusts are found in India: Desert locust, Migratory locust, Bombay Locust and Tree locust
o Desert locusts are usually restricted to the semi-arid and arid deserts of Africa, the Near East and South West Asia that receive less than 200 mm of rain annually.
- They lay eggs in damp soil in the bare ground, which is rarely found in areas with dense vegetation
SUPER YEAR FOR BIODIVERSITY
- The year 2020 is the “Super Year For Biodiversity”, as the Strategic Plan for Biodiversity with 20 global Aichi targets adopted in 2010 ends in 2020.
Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD)
- The CBD is an international multilateral treaty which was opened for signature in 1992 at the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (the Rio "Earth Summit").
- It has 3 main objectives:
o The conservation of biological diversity.
o The sustainable use of the components of biological diversity.
o The fair and equitable sharing of the benefits arising out of the utilization of genetic resources.
- The CBD has 196 parties and India is one of them.
GAS LEAK AT VIZAG
- Styrene gas leaked from Vishakhapatnam based LG Polymers India Pvt Ltd. factory causing multiple deaths.
Legal Provisions related to Industrial Disasters
- Environment (Protection) Rules, 1986
- Hazardous Waste (Management Handling and Transboundary Movement) Rules, 1989
- Manufacture, Storage and Import of Hazardous Chemicals Rules, 1989
- Chemical Accidents (Emergency, Planning, Preparedness and Response) Rules, 1996 Factories Amendment Act, 1987
- Public Liability Insurance Act, 1991
Judicial Pronouncements w.r.t setting the liability in case of Industrial Disasters
- Doctrine of Absolute Liability: This concept evolved in India after the case of M.C Mehta vs Union of India (1986), famously known as Oleum Gas Leak case.
o According to this doctrine as defined by the Supreme Court, the enterprise owes an absolute and non-delegable duty to the community to ensure that no harm results to anyone on account of hazardous or inherently dangerous nature of the activity which it has undertaken.
- The rule of strict liability: Till the MC Mehta case, India also followed the concept of ‘strict liability’.
o Under the “strict liability principle”, a party is not liable and need not pay compensation if a hazardous substance escapes his premises by accident or by an “act of God’” among other circumstances.
INDIA’S FIRST DOLPHIN OBSERVATORY
- The Bihar government is setting up India’s first observatory for the Gangetic dolphins in Bhagalpur district.
- The observatory is constructed at Vikramshila Gangetic Dolphin Sanctuary (VGDS).
o Observatory will aim to promote eco-tourism.
o There would be no adverse impact on the river’s ecology as the observatory is being constructed on a Sultanganj-Aguwani Ghat bridge over the Ganga.
About Gangaetic dolphin
o IUCN Status: Endangered
o They prefer deep waters, in and around the confluence of rivers. They can only live in freshwater and are essentially blind.
o They are reliable indicator of the health of the entire river ecosystem.
o It is also National Aquatic Animal of India.
Other dolphins found in India
- Indus River Dolphin
- Irrawaddy Dolphin (Snubfin dolphin)
- Indian Ocean humpback dolphin
MISCELLANEOUS
GEOGRAPHICAL INDICATION (GI) TAG
Recently, GI tags were awarded to multiple products.
- GI Tag is a sign used on products that have a specific geographical origin and possess qualities or a reputation that are due to that origin.
o These are regulated under Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act,1999 and given by Controller General of Patents, Designs and Trademarks who is Registrar of Geographical Indications.
o GI is covered under Trade Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) Agreement.
Products to which GI tags were granted
- Kashmir Saffron
o It is cultivated in Karewas (highlands) of Jammu & Kashmir.
o It is only saffron in world grown at an altitude of 1,600 m to 1,800 m.
- Kovilpatti Kadalai Mittai (Tamil Nadu)
- Hao (black rice of Manipur)
- Gorakhpur terracotta
o It is a centuries-old traditional art form, where the potters make various animal figures like, horses, elephants, camel, goat, ox, etc. with hand-applied ornamentation.
- Sohrai Khovar painting
o It is a traditional and ritualistic mural art being practised by local tribal women in the area of Hazaribagh district of Jharkhand.
o It is done during local harvest and marriage seasons using local, naturally available soils of different colours.
- Telia Rumal (Telangana)
o It involves intricate handmade work with cotton loom displaying a variety of designs and motifs in three particular colours — red, black and white.
WORLD WAR 2
- US, Europe and Russia celebrated May 8 (May 9 in Russia) as Victory Day to mark 75th anniversary of end of Second World War in Europe.
About Second World War
- It was total war and most destructive war that world has observed till date.
- Primary combatants
o Axis nations - Germany, Italy, Japan
o Allied nations - Great Britain (and its Commonwealth nations), France, Soviet Union and United States.
PURANDARA DASA
- Karnataka government will commence field research at Keshavapura in Karnataka to solve the mystery regarding the birth place of Purandara Dasa.
- Till now, it was believed that Purandara Dasa was born in Purandaragarh near Pune, Maharashtra.
- However, an expert committee constituted by Karnataka Government reported that there is enough evidence to suggest Keshavapura as his birth place and recommended further research.
About Purandara Dasa
- Purandara Dasa (1484- 1564) was a saint, poet and singer during the Vijayanagara empire.
- He is regarded as the ‘Pitamaha’ of Carnatic music. His systemized method of teaching Carnatic music is followed till present day.
SAMPLE REGISTRATION SYSTEM (SRS) BULLETIN RELEASED
- SRS is a demographic survey for providing reliable annual estimates of IMR, birth rate, death rate and other fertility and mortality indicators at the national and sub-national levels.
- SRS is conducted by Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner under Ministry of Home Affairs.
Key highlights
- Infant Mortality Rate (IMR) declined to 32 in 2018 from 129 in 1971.
o Madhya Pradesh has highest IMR at 48 and Nagaland lowest at 4.
o In last 10 years, IMR declined by about 35% in rural areas and about 32% in urban areas.
o IMR is number of deaths under one year of age occurring for 1000 live births in a given year.
- Birth rate (BR): declined from 36.9 in 1971 to 20.0 in 2018.
o Bihar has the highest BR at 26.2 and Andaman and Nicobar Islands has lowest BR of 11.2.
o Rural-urban differential has also narrowed. However, birth rate has continued to be higher in rural areas.
O BR is number of live births per 1000 of population per year.
- Death rate (DR): Declined to 6.2 in 2018 from 14.9 in 1971.
o Chhattisgarh has highest death rate at 8 and Delhi has a rate of 3.3.
o DR Number of deaths per 1000 people per year.
DIAMER-BASHA DAM
- China and Pakistan signed an accord to construct this Dam in Gilgit-Baltistan region.
- It is to be constructed on the River Indus with a capacity of 4,500 MW.
- India had objected to the construction of the dam repeatedly as it falls into the Indian territory of northern Gilgit-Baltistan region.
VANDE BHARAT MISSION
- It is India’s largest repatriation operation to bring home Indian nationals stranded abroad due to COVID-19 lockdown.
- People are brought back in flights by Air India and also by Indian Navy (from Sri Lanka and Maldives)
OPERATION SAMUDRA SETU (SEA BRIDGE)
- It has been launched by Indian Navy as a part of national effort to repatriate Indian citizens from overseas.
- As part of Phase-1, Indian Naval Ships Jalashwa and Magar are presently enroute to Maldives to commence evacuation operations
EVENTBOT MOBILE BANKING TROJAN
- Recently, The Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In) issued an advisory warning to people against a trojan called EventBot.
- The EventBot is a mobile Banking Trojan and information stealer that specifically targets the financial apps on the phone and the financial data of its victim.
o A Trojan horse or Trojan is a type of malware that is often disguised as legitimate software
FLORENCE NIGHTINGALE
- 200th birth anniversary of Florence Nightingale, founder of modern nursing was celebrated on May 12.
- Florence Nightingale (1820-1910) also known as “The Lady with the Lamp” was a British nurse, social reformer and statistician best known as the founder of modern nursing.
- The International Nurses Day is observed annually on May 12 commemorating her birth and celebrates the important role of nurses in health care
IRAN’S NEW CURRENCY
- Iran's parliament has passed a bill to change the monetary unit from ‘Rial’ to the popularly used ‘toman’.
- Each toman will be worth 10,000 Rials under the new system.
